Group A streptococcal infections: 12th update on seasonal activity in England
Updated 29 June 2023
Applies to England
Data to 26 March 2023.
Main points
Notifications and GP consultations of scarlet fever in England identified exceptional levels of activity in the early phase of the season. While rapid declines were seen in the second half of December, numbers of scarlet fever notifications remained above usual seasonal levels; they are now within usual seasonal levels.
Notifications of invasive group A streptococcus (iGAS) disease remain above the range expected for this time of year. Relatively high rates of iGAS infection in children have been observed with increases in adults occurring in recent weeks.
Medical practitioners were alerted to this early increase in incidence and elevated iGAS infection in children on 2 December 2022. Given the potential for severe presentations, scarlet fever cases should be treated promptly with antibiotics to limit further spread and reduce potential complications in cases and their close contacts.
Clinicians should continue to be alert to the severe complications of GAS and maintain a high degree of clinical suspicion when assessing patients, particularly those with preceding viral infection (including chickenpox) or who are close contacts of someone with scarlet fever.
Updated UK public health guidance on the management of close contacts of iGAS cases in community settings in community settings was published on 15 December 2022 and updated on 2 March 2023, with public health action extended to include patients with probable invasive GAS infection and additional close contact groups now recommended for antibiotic prophylaxis.
National guidance on the management of scarlet fever outbreaks highlights essential tools to limit spread: prompt notification of scarlet fever cases and outbreaks to UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) health protection teams (HPTs), collection of throat swabs (prior to commencing antibiotics) when there is uncertainty about the diagnosis and exclusion of cases from school or work until 24 hours of antibiotic treatment has been received.
Data presented within this seasonal activity update is based on data available as of 29 March 2023 and present data to 26 March 2023 (the end of week 12). Numbers presented in this report may change when updated data becomes available. A further seasonal update report will be published in April. Weekly notifiable disease reports are published each week throughout the year to provide a regular update of scarlet fever notifications.
Key definitions are available at the end of the report.
Scarlet fever
Higher than expected scarlet fever activity was noted during the early part of summer 2022 in England. Notifications during the early part of the current season increased to exceptional levels (Figure 1). (Seasons are defined as running from week 37 (mid-September) in one year to week 36 in the following year.)
A total of 52,183 notifications of scarlet fever were received from week 37 to week 12 of this season (2022 to 2023) in England, with a pre-Christmas peak of 10,068 notifications in week 49. This compares with an average of 8,473 (range 819 to 17,464) for this same period (weeks 37 to 12) in the previous 5 years. Increased health seeking behaviour as a result of national alerts is likely to have contributed to the increased reports. The last peak season for scarlet fever notifications was 2017 to 2018 when 30,768 reports were received across the entire season.
Notifications in the early weeks of 2023 remain lower than those reported in December 2022, and since week 8 remain within the expected range for this time of year. There have been 15,767 scarlet fever notifications in the first 12 weeks of 2023, higher than the average for this point in the calendar year (5,612, range 340 to 13,262 between 2018 and 2022).
Figure 1. Weekly scarlet fever notifications in England, by season, 2017 to 2018 onwards (weeks 37 to 12)
Note: Data for the current season goes up to week 12 (26 March 2023); data for the most recent weeks may change as further notifications are received and processed, represented by a dotted line between weeks 47, 2022 and 12, 2023.
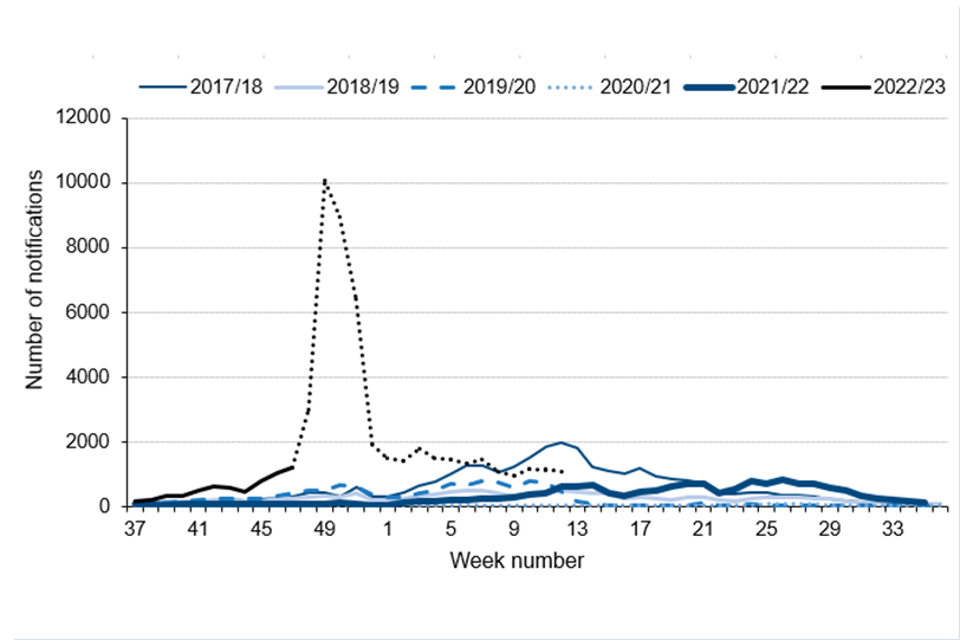
Scarlet fever notifications to date this season showed considerable variation across England, ranging between 73.2 (West Midlands) and 132.7 (East Midlands) per 100,000 population (Table 1).
Table 1. Number and rate per 100,000 population of scarlet fever and iGAS notifications in England: week 37 to week 12 of the 2022 to 2023 season
Notes: More details of an improved processing method implemented since the 10th update report are described in the data and methods section of this report. Week 37 to week 12 covers the period 12 September 2022 to 26 March 2023.
| Region | Number of cases of scarlet fever | Rate of scarlet fever | Number of cases of iGAS | Rate of iGAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| East of England | 5,242 | 79.0 | 262 | 3.9 |
| East Midlands | 6,477 | 132.7 | 260 | 5.3 |
| London | 6,817 | 77.5 | 305 | 3.5 |
| North East | 2,117 | 80.0 | 157 | 5.9 |
| North West | 8,568 | 115.4 | 325 | 4.4 |
| South East | 7,591 | 84.3 | 461 | 5.1 |
| South West | 5,019 | 87.9 | 279 | 4.9 |
| West Midlands | 4,359 | 73.2 | 255 | 4.3 |
| Yorkshire and the Humber | 5,986 | 109.2 | 347 | 6.3 |
| England | 52,183 | 92.3 | 2,651 | 4.7 |
Invasive group A streptococcal infection
Laboratory notifications of iGAS infection so far this season (weeks 37 to 12, 2022 to 2023) remain considerably higher than expected (Figure 2). A total of 2,651 notifications of iGAS disease were reported through laboratory surveillance in England, higher than recorded over the last 5 seasons for the same weeks (average 1,030, range 465 to 1,565 notifications; Figure 2), with a weekly high of 212 notifications in week 52 (26 December 2022 to 1 January 2023).
There have been 1,244 iGAS laboratory notifications in the first 12 weeks of 2023, higher than the average for this point in the calendar year (535; range 208 to 968 between 2018 and 2022).
Figure 2. Weekly laboratory notifications of invasive GAS, England, by season, 2017 to 2018 onwards (weeks 37 to 12)
Notes: In this graph, the most recent weeks of the 2022 to 2023 season are expected to increase due to lags in reporting timelines from laboratories. The decline in recent weeks should be interpreted with caution, normal processing and reporting timeframes mean that increases in laboratory reports are expected – represented by a dashed line between weeks 10 and 12. More details of the improved processing method implemented since the 10th update report are described in the data and methods section of this report.
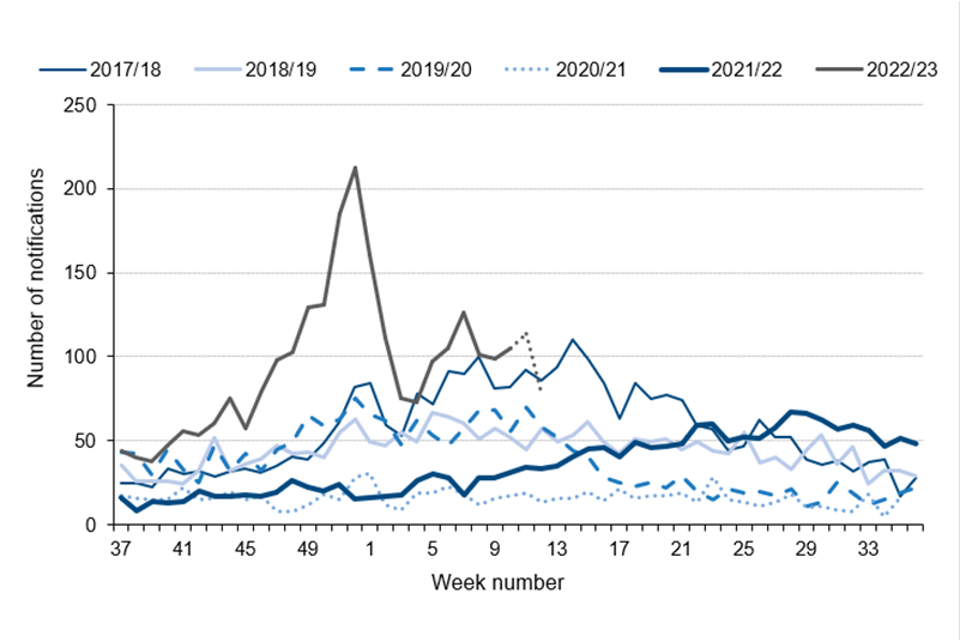
While laboratory notifications remain lower than the high recorded in week 52, levels of activity remain above what would be expected at this point in the season. Further increases are possible in the coming weeks as we move towards the usual time of year for peak activity, typically occurring between weeks 6 and 18.
During the current season to date, the highest rates were reported in the Yorkshire and Humber region (6.3 per 100,000 population), followed by the North East (5.9 per 100,000) and South East region (5.1 per 100,000); see Table 1.
The highest rate was in those aged 75 years and over age group (12.4 per 100,000), followed by those aged 1 to 4 years (12.1 per 100,000) and those aged under 1 year (10.2 per 100,000); see Table 2.
Table 2. Rate per 100,000 population of iGAS notifications in England by age group, week 37 to week 12 in the 2022 to 2023 season versus the 2017 to 2018 season
Note: In this table the current 2022 to 2023 season covers weeks 37 to 12, whereas the 2017 to 2018 season data covers the full season, weeks 37 to 36. More details on an improved processing method implemented since the 10th update report are described in the data and methods section of this report.
| Age group (years) | 2022 to 2023 season (weeks 37 to 12): number of cases | 2022 to 2023 season (weeks 37 to 12): rate per 100,000 population | 2017 to 2018 (full season): number of cases | 2017 to 2018 (full season): rate per 100,000 population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aged 1 year and under | 59 | 10.2 | 78 | 12.2 |
| 1 to 4 | 299 | 12.1 | 194 | 7.1 |
| 5 to 9 | 189 | 5.7 | 112 | 3.2 |
| 10 to 14 | 65 | 1.9 | 37 | 1.1 |
| 15 to 44 | 513 | 2.4 | 622 | 2.9 |
| 45 to 64 | 534 | 3.7 | 613 | 4.3 |
| 65 to 74 | 380 | 6.8 | 468 | 8.4 |
| 75 and over | 606 | 12.4 | 773 | 16.7 |
| Total | 2,651 | 4.7 | 2,898 | 5.2 |
The median age of patients with iGAS infection so far this season was 52 years (range under 1 year to 102 years), slightly lower than the range seen at this point in the preceding 5 seasons (aged 52 to 58 years).
Twenty one per cent of iGAS infections reported so far this season are in children (aged 15 years and under), higher than the range seen for the past 5 seasons (4% to 15%). The slight increase in median age compared to earlier in the season, and the percentage of iGAS that are in children (aged under 15 years), continue to indicate a slight change towards more cases occurring in the older adult age groups (aged 65 years and over).
So far this season 355 deaths (from any cause) have been recorded within 7 days of an iGAS infection diagnosis (176 occurring in 2023), with 65% (n=230) of the recorded deaths being in those aged 65 years and over, and 9% (n=32) in children aged 10 years and under (Table 3). The case fatality rate (CFR) to date is higher than in recent seasons, although it does vary by age group with the CFR being more elevated in elderly people. Elevations in rates of iGAS infection in children in this early part of this season have resulted in an increased number of deaths over a relatively short period, with 38 deaths in children aged under 15 years identified to date for weeks 37 to 12.
There have been 635 iGAS reports in children under 18 years in the season to date (24% of iGAS reports), with 40 deaths being recorded in this age group (CFR of 6.7%).
Antimicrobial susceptibility results obtained from routine laboratory surveillance so far this season indicate tetracycline resistance in 12% of GAS sterile site isolates; this is lower than at this point last season (39%). Susceptibility testing of iGAS isolates against erythromycin indicated 4% were found resistant (compared with 15% last season), and, for clindamycin, 4% were resistant at this point in the season (13% last season). Isolates remained universally susceptible to penicillin.
Analysis of iGAS isolate typing data continues to indicate a diverse range of emm gene sequence types identified this season. The results indicate emm 1.0 remains the most common (54% of referrals), followed by emm 12.0 (11%) and emm 89.0 (4%), compared with 23%, 7% and 10% at the same point in the 2017 to 2018 season, respectively. In children (aged under 15 years) emm 1.0 and emm 12.0 have dominated this season, accounting for 65% and 16% respectively (compared with 28% and 8% at this point in the 2017 to 2018 season).
Table 3. Case fatality rate (%) for deaths (all causes) within 7 days of an iGAS specimen, by age group in England for the current season and the previous 5 seasons
Note 1: The total may include notifications where the age was unknown. The case fatality rate is the percentage of deaths within 7 days of iGAS infection diagnosis for cases where follow-up has been possible. CFR should be interpreted with caution given the small numbers involved. The current season data (2022 to 2023) covers week 37 to week 12 (12 September 2022 to 26 March 2023). The prior seasons cover the whole season (weeks 37 to 36). ‘Pandemic seasons’ presents data for the 2019 to 2020 and 2020 to 2021 seasons combined. Note 2: Due to a data correction, 1 death in the under-1-year age group in the 2022 to 2023 season no longer meets the reporting definition for deaths within 7 days, leading to a reduction in deaths compared to the previous report.
| Age group (years) | 2017 to 2018 season % CFR | 2018 to 2019 season % CFR | Pandemic seasons (2019/2020 and 2020/2021) % CFR | 2021 to 2022 season % CFR | 2022 to 2023 season (weeks 37 to 12) % CFR | 2022 to 2023 season: number of deaths (all causes) within 7 days of iGAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aged 1 year and under | 5.6% | 2.1% | 7.7% | 3.8% | 5.3% | 3 |
| 1 to 4 | 4.7% | 6.1% | 9.0% | 5.9% | 6.5% | 18 |
| 5 to 9 | 9.9% | 4.6% | 2.7% | 10.6% | 6.1% | 11 |
| 10 to 14 | 7.9% | 8.7% | 23.8% | 0.0% | 10.3% | 6 |
| 15 to 44 | 4.1% | 1.7% | 2.5% | 2.3% | 6.6% | 32 |
| 45 to 64 | 8.4% | 8.6% | 9.3% | 9.7% | 10.7% | 55 |
| 65 to 74 | 13.5% | 8.8% | 13.8% | 13.1% | 16.8% | 61 |
| 75 and over | 24.4% | 16.8% | 19.9% | 18.1% | 28.6% | 169 |
| Total | 12.4% | 9.1% | 11.3% | 10.0% | 14.0% | 355 |
Discussion
While scarlet fever notifications in early 2023 remained elevated, weekly rates of scarlet fever notification and GP consultations have fallen to within usual levels for this point in the season. In contrast, levels of invasive GAS disease remain elevated. Monitoring will continue over the coming weeks to identify potential increases in line with the normal seasonal pattern.
Public and healthcare professional alerts issued in week 48 (2 December 2022) may have succeeded in bringing people forward for clinical assessment and treatment, resulting in the sharp increase in notifications in week 49, and reducing onward transmission.
The rate of iGAS infection notifications across the season showed weekly incidence trending above what would be expected during the first part of the season, particularly during December 2022 but continuing into early 2023.
Investigations are continuing following reports of an increase in lower respiratory tract GAS infections, particularly empyema, in children during November and December 2022 (1). The current emm types have been circulating for many years. While a new strain of emm1 (M1UK) was documented as having emerged and expanded in the last decade, its role (if any) in driving the current high levels of iGAS in children remains uncertain. At present, the weekly rate of iGAS in individuals over 75 years is higher than has been seen at this point in the season in pre-pandemic periods; the CFR at this point in the season is higher than for previous years, with emm1 dominant in this age group. Detailed genomic and biological investigations are under way to investigate any differences in the pathogen being seen this season.
The elevated iGAS levels in children compared to the period when pandemic control measures were in place is likely to be a consequence of the heightened scarlet fever activity given the crossover of strains associated in both presentations (2, 3). Reduced exposure to GAS infections during the pandemic is also likely to have led to increased susceptibility to these infections in children, in view of the very low levels seen during the pandemic. Prompt treatment of scarlet fever with antibiotics is recommended to reduce risk of possible complications and limit onward transmission.
Public health messaging to encourage contact with NHS 111 or GP practices for clinical assessment of patients with specific symptoms suggestive of scarlet fever has been issued along with reminders to provide ‘safety netting’ advice for parents indicating signs and symptoms of deterioration, particularly for children with respiratory viral infection. GPs and other frontline clinical staff are also reminded of the increased risk of invasive disease among household contacts of scarlet fever cases (4, 5).
Clinicians should continue to maintain a high index of suspicion in relevant patients for invasive disease as early recognition facilitates prompt initiation of specific and supportive therapy for patients with iGAS infection.
Relevant guidelines and information can be found on GOV.UK and elsewhere as follows:
-
Prevention and control of group A streptococcal infection in acute healthcare and maternity settings
-
Weekly notifiable disease reports are published for a timelier update
Invasive disease isolates and also non-invasive isolates from suspected clusters or outbreaks should be submitted to:
Staphylococcus and Streptococcus Reference Section
Antimicrobial Resistance and Healthcare Associated Infections (AMRHAI)
UK Health Security Agency
61 Colindale Avenue
London
NW9 5HT
Data sources and methods
Scarlet fever notification data was extracted from the notifications of infectious diseases (NOIDs) reports. Data for England was extracted on 29 March 2023. Weekly totals include a few scarlet fever notifications identified in port health authorities; this will mean that the regional totals will not equal the season total for England.
Invasive GAS laboratory notification data was extracted from the UKHSA Second Generation Surveillance System (SGSS) and combined with specimen referrals to the Staphylococcus and Streptococcus Reference Section to produce a total number of episodes for England. Data was extracted on 29 March 2023.
The sharp increase in scarlet fever and other group A strep infections alongside increased awareness and vigilance among clinicians has led to a significant rise in scarlet fever notifications in recent weeks. This has resulted in a backlog of notifications of scarlet fever cases being entered into the national database after being processed.
A season runs from week 37 in one year to week 36 in the following year (mid-September to mid-September). The 2022 to 2023 season data within this report covers 12 September 2022 to 26 March 2023.
All-cause deaths within +/- 7 days: reported date of death (obtained from tracing against the NHS SPINE where patient information is available) is compared to the date of iGAS specimen in a patient. This includes those where the difference between the 2 dates is ≤ 7 days, or ≥ minus 7 days (to include those potentially diagnosed via post mortem). Follow-up was not possible for all reported iGAS cases, primarily due to poor identifier (NHS number and date of birth) completion. In addition, not all iGAS cases have the full 7-day follow-up period for case fatality assessment. CFR should be interpreted with caution given the small numbers involved.
An improved method of patient iGAS episode de-duplication was implemented in the 10th update report, and is to be continued to be applied for all subsequent reports. The new method corrected an error which resulted in a small number of records being counted more than once in the iGAS episode analyses in the prior reports. This change does not impact the mortality data. The new method led to a 6% reduction in iGAS episodes recorded in the 2022 to 2023 season, impacting some regions more than others in the earlier seasonal update reports. Please refer to the appendix tables for a detailed comparison.
Population rates are calculated per 100,000 using the relevant year’s ONS mid-year population estimate. Rates have been updated to reflect the recent release of the 2021 mid-year population estimates.
The M protein gene (emm) encodes the cell surface M virulence protein.
Prior to the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, there were a number of seasons with elevated incidence of scarlet fever and iGAS, in particular, the 2017 to 2018 season; this has been used as comparison point for the trends seen in the current season. During the pandemic there was an unprecedented reduction in the number of scarlet fever and iGAS notifications, affecting the 2019 to 2020 season, and the 2021 to 2022 season.
References
1. Guy R, Henderson KL, Coelho J, Hughes H, Mason EL, Gerver SM and others (2023). Increase in invasive group A streptococcal infection notifications, England, 2022. Eurosurveillance: volume 28, issue 1.
2. Chalker V, Jironkin A, Coelho J, Al-Shahib A, Platt S, Kapatai G, and others (2017). ‘Genome analysis following a national increase in scarlet fever in England 2014’. BMC Genomics: volume 18 number 1, page 224
3. Al-Shahib A, Underwood A, Afshar B, Turner CE, Lamagni T, Sriskandan S, and others (2016). Emergence of a novel lineage containing a prophage in emm/M3 group A Streptococcus associated with upsurge in invasive disease in the UK’. mGen; volume 2 number 11
4. Lamagni T, and others (2018). ‘Resurgence of scarlet fever in England, 2014–16: a population based surveillance study’. The Lancet Infectious Diseases: volume 18, number 2, pages 180 to 187
5. Watts V, and others (2019). ‘Increased risk for Invasive Group A Streptococcus disease for household contacts of scarlet fever cases, England, 2011–2016’. Emerging Infectious Diseases: volume 25, number 3, pages 529 to 537
Acknowledgements
These reports would not be possible without the weekly contributions from microbiology colleagues in laboratories across England, without whom there would be no surveillance data.
Feedback and specific queries about this report are welcome via [email protected]
