Weekly statistics for NHS Test and Trace (England) and coronavirus testing (UK): 30 July to 5 August
Updated 18 August 2020
Main points
Since NHS Test and Trace launched (28 May to 5 August):
5,212 new people tested[footnote 1] positive for coronavirus (COIVD-19) in England in between 30 July and 5 August. This is an increase of 4% in number of positive cases compared to the previous week. The number of people tested has increased by 12% in the same time period.
Testing turnaround times for pillar 2 (swab testing for the wider population) increased compared to the previous week. 67.4% of in person tests were returned within 24 hours compared to 76.9% the previous week. 43.6% of home/satellite tests were returned within 48 hours compared to 72.9% the previous week.
4,973 people were transferred to the contract tracing system between 30 July and 5 August, an increase of 7% compared to the previous week, in line with the upward trend in people testing positive since the beginning of July.
Of those transferred to the contact-tracing system between 30 July and 5 August, 79.7% were reached and asked to provide information about their contacts. This has remained broadly constant since the middle of June.
20,638 people were identified as coming into close contact with someone who has tested positive between 30 July and 5 August, a 6% increase from the previous week. Of these, 74.2% were reached and asked to self-isolate, compared to 72.4% in the previous week. This percentage has remained approximately constant for the last 4 weeks.
For coronavirus (COVID-19) testing in the UK:
The number of tests processed in the UK, across all pillars, increased by 25.1%, between the week from 30 July to 5 August and the previous week, to 1,210,318 tests.
Testing capacity increased by 1.6% between 30 July and 5 August to 2,386,016 tests per week.
Introduction
The Department for Health and Social Care publishes weekly statistics on NHS Test and Trace (England) and now, for the first time, coronavirus (COVID-19) testing in the UK, across all 4 testing pillars. The purpose of this data is to provide a weekly update on the implementation and performance of NHS Test and Trace in England and Testing in the UK.
For NHS Test and Trace (England), this includes:
Testing
- people tested for coronavirus (COVID-19), England
- people testing positive for coronavirus (COVID-19), England
- time taken for test results to become available, England
Contact tracing
- people transferred to the contact-tracing system, and the time taken for them to be reached, England
- close contacts identified for complex and non-complex cases, and the time taken for them to be reached, England
For coronavirus (COVID-19) testing in the UK, this includes:
- lab testing capacity, UK
- number of tests sent out, UK
- number of tests processed, UK
Data collected for NHS Test and Trace is primarily for operational purposes and was not designed to track the spread of the virus. Studies into the spread of the virus in the UK are carried out by the Office for National Statistics (ONS). A list of data sources relating to the coronavirus pandemic in the UK can be found at Coronavirus (COVID-19) statistics and analysis.
A full explanation of the data sources and methods used to produce these statistics can be found in the additional methodology document for NHS Test and Trace statistics and the coronavirus (COVID-19) testing data methodology
Revisions to figures previously published
NHS Test and Trace statistics (England)
Figures for people tested and people testing positive for coronavirus (COVID-19) in previous releases have been revised. These revisions are because:
- there are sometimes delays in laboratories submitting data to PHE
- quality checks are conducted on the data to refine figures over time
Figures for pillar 1 testing turnaround times are not routinely revised as only minor changes occur to past weeks post publication. Figures are only revised when substantial changes occur.
Figures for pillar 2 testing turnaround times in previous releases have been revised. These revisions are because:
- an improvement in data quality has led to better identification of the location of Mobile Testing Units in England, leading to an increase in the identification of tests conducted at those locations
- the figures presented are based on a data-cut several days after the end of the reporting period – some tests may continue to be being processed after this period and therefore data may need to be revised over time
Figures for contact tracing in previous releases have been revised. These revisions are because the figures presented are based on a data cut several days after the end of the reporting period, to give time for cases reported towards the end of the 7-day period to have an outcome. Some cases may continue to be in progress after this period, and therefore data may need to be revised over time.
Further details are available in the NHS Test and Trace statistics methodology.
Coronavirus (COVID-19) testing in the UK
For tests processed and tests sent out, weekly totals reflect the sum of actual daily counts reported for the previous week.
Each week there may be corrections to previously reported figures, for example, where labs (or studies under pillar 4) returned the results late or duplicates were identified and removed. These corrections are reflected in the cumulative figures. This means that previously published weekly counts will not necessarily sum to the latest cumulative figure. It also means that the latest cumulative count may not match the previous week’s cumulative count plus this week’s weekly count.
NHS Test and Trace
NHS Test and Trace was launched in England on 28 May and ensures that anyone who develops symptoms of coronavirus (COVID-19) can quickly be tested to find out if they have the virus. It then helps trace recent close contacts of anyone who tests positives for coronavirus and, if necessary, notifies them that they must self -isolate at home to help stop the spread of the virus. The flow of how people move through the NHS Test and Trace service is shown in Figure 1.
More information about NHS Test and Trace can be found at NHS Test and Trace: how it works.
Testing in England
NHS Test and Trace starts with an individual taking a test, either in pillar 1 (testing in hospitals and outbreak locations, pillar 2 (national swab testing) or pillar 4 (prevalence studies). Those who go on to test positive will have their case transferred to NHS Test and Trace for contact tracing.
NHS Test and Trace is for England only, therefore the figures in this section are given for England. Figures for UK testing are given in the section coronavirus (COVID-19) testing in the UK and information on contract tracing in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland can be found directly from Public Health Scotland, the Welsh government and the Northern Ireland Public Health Agency.
Figure 1: flowchart showing how people move through the NHS Test and Trace service
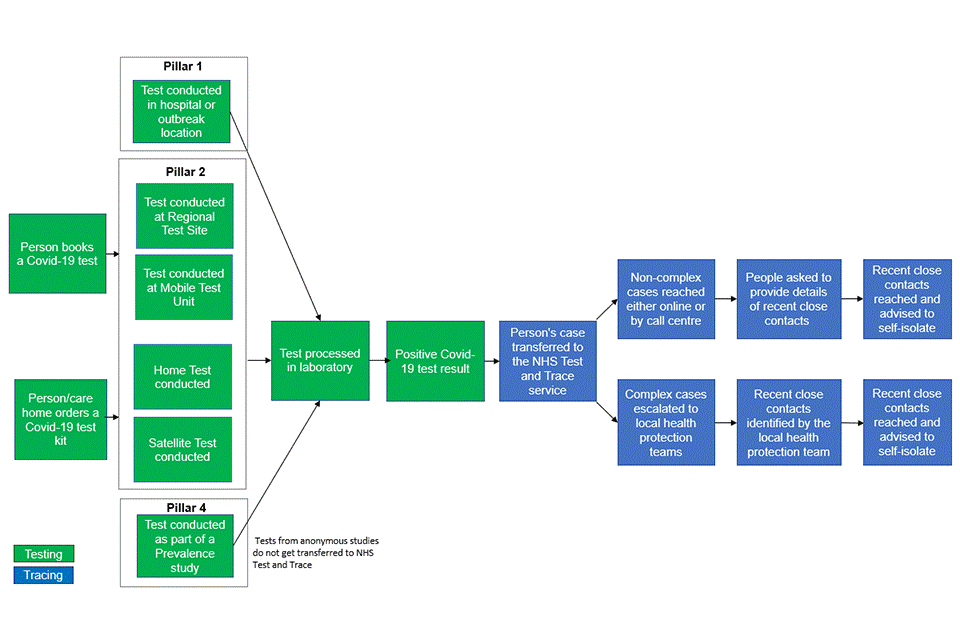
People tested, England
Between 30 July and 5 August, 438,404 people were newly tested for coronavirus (COVID-19), an increase of 12% from the previous week. 5,212 new people had a positive result, an increase of 4% from the previous week[footnote 2]
Since Test and Trace launched at the end of May, 3,529,188 people have been tested, of which 65.5% were tested under pillar 2 (national swab testing) and 34.5% under pillar 1 (testing in hospitals and outbreak locations). The number of people tested decreased from the end of May until mid-June and has since increased each week up to the latest week. The number of people tested under pillar 2 has increased by 16% since the previous week, in comparison to people tested under pillar 1 which has increased by 4%.
Figure 2: number of people newly tested for COVID-19 by pillar, England
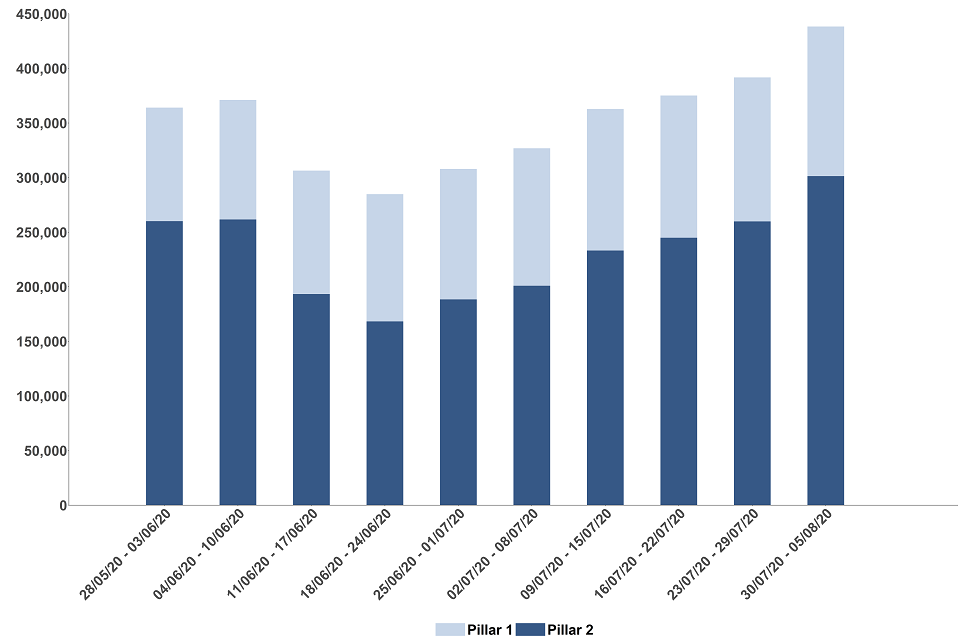
The data for the most recent weeks can be found in the annex, table 1.
Since Test and Trace launched at the end of May, 53,427 people newly tested positive for COVID-19 , 75.8% of these positive cases were tested under pillar 2 in comparison to 24.2% under pillar 1.[footnote 3] There has been a gradual decline in positive cases under pillar 1 each week, including a 17.3% decrease between 30 July and 5 August compared to the previous week. There has been an upward trend in positive cases under pillar 2 since the end of June with an increase of 7.6% between 30 July and 5 August compared to the previous week. Overall the total number of people testing positive has been increasing since the start of July.
Figure 3: number of people newly testing positive for COVID-19 by pillar, England
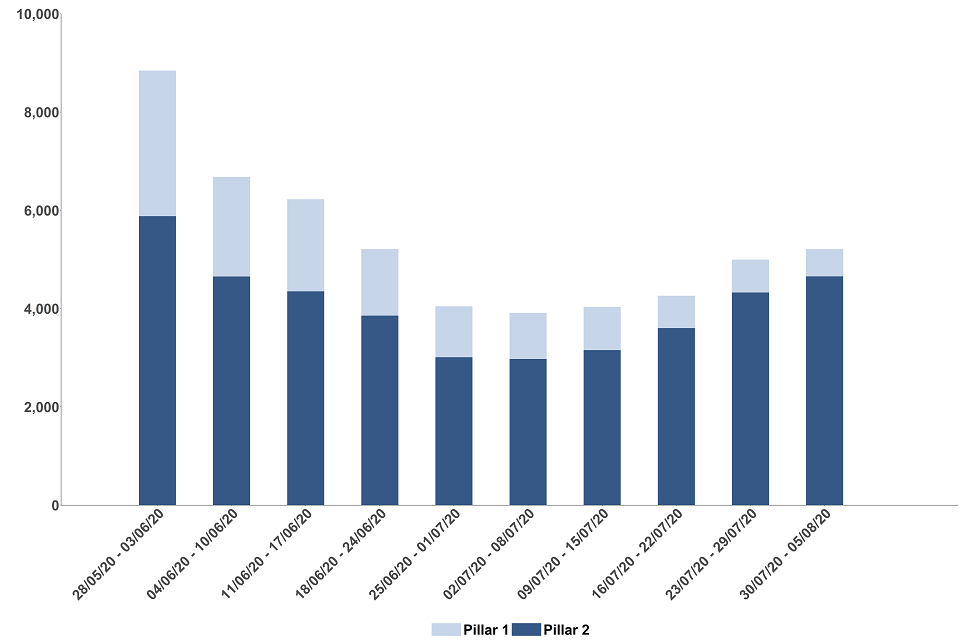
The data for the most recent weeks can be found in the annex, table 1.
Pillar 1 testing turnaround times, England
Most pillar 1 tests are conducted in a hospital setting, and it is therefore not practical for those administering the tests to record the exact time that a test was taken. Therefore, the time taken to receive a coronavirus (COVID-19) test result is measured from the time that a test is received by a laboratory for processing to the time when the results are published to the Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS).
The total tests given in figures for pillar 1 turnaround times is not the same as the number of tests processed in pillar 1 as study samples and tests from private laboratories do not report data on turnaround times. This data is only available from 9 July (week 7 onwards). More details can be found in the methodology document.
9 out of 10 pillar 1 test results were made available within 24 hours of the laboratory receiving the test. This proportion has remained similar since reporting began from 9 July
Figure 4: number of pillar 1 test results by whether they were made available within 24 hours of the laboratory receiving the test, England
The data for the most recent weeks can be found in the annex, table 2.
Pillar 2 testing turnaround times, England
There are various routes for getting tested within pillar 2 (national swab testing). Data on the time taken to receive a COVID-19 test result for pillar 2 is split up to reflect this, as this impacts on the turnaround times.[footnote 4] These routes include:
-
regional test sites – includes drive-through testing centres with limited walk-up facilities. This also includes Local Test Sites, which are similar to regional test sites but specifically for walk ups
-
mobile testing units – travel around the UK to increase access to COVID-19 testing. They respond to need, travelling to test people at specific sites including care homes, police stations and prisons
-
satellite test centres – includes test kits provided directly to ‘satellite’ centres at places like hospitals or care homes that have a particularly urgent or significant need
-
home test kits – delivered to someone’s door so they can test themselves and their family without leaving the house
Turnaround times are measured and reported in 2 ways, time taken from booking a test and from taking a test to receiving a test result. Both measures are given in the data tables on the weekly publication collection page, however only time from taking a test is discussed below.
More information on these definitions is in the terminology section.
The total tests reported for pillar 2 turnaround times is not the same as the number of tests processed in pillar 2 as test processed is available for the UK (rather than for England only). In addition, they are reporting on the number of tests at different stages in the process.
Further detail is given in the NHS Test and Trace statistics methodology.
After someone takes a test, it is transported to a laboratory for processing. There are normal fluctuations in this operational process which can sometimes cause the time taken to receive a test result to go over 24 hours, but still be turned around the next day. Where appropriate therefore we also provide the number of tests turned around the day after a test was taken.
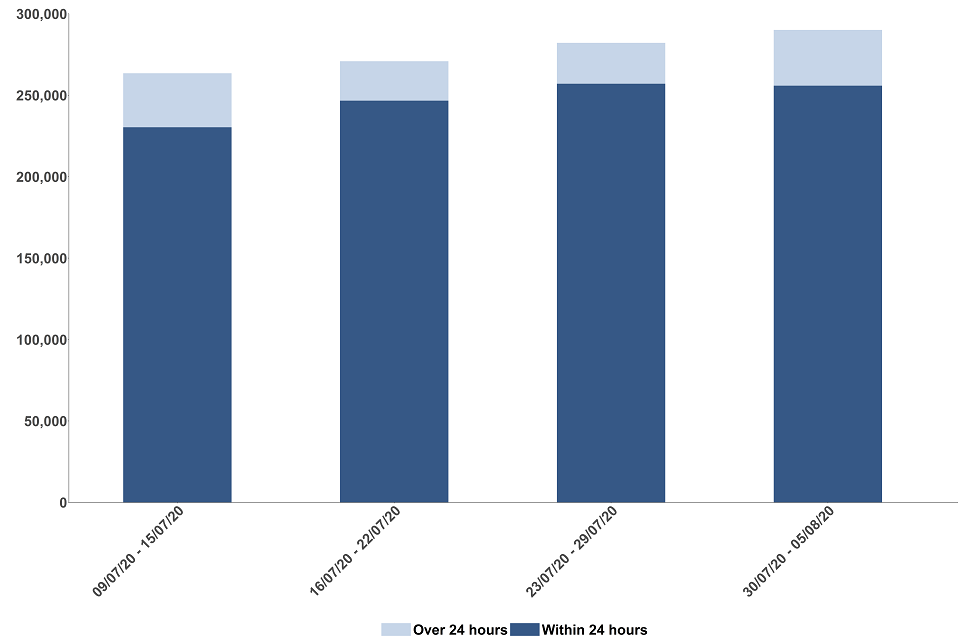
The time taken to receive a test result after taking a test decreased rapidly in the first month of Test and Trace but has increased in the latest week
All routes have seen a reduction in the time taken to receive a test result since Test and Trace began with in person tests having had the most substantial improvements. Between 30 July and 5 August, 67.4% of test results were received within 24 hours for in person tests (mobile testing units and regional test centres) compared to 11.0% when Test and Trace began at the end of May. If we consider the day the test was taken, 93.6% of in-person tests results were received the next day after the test was taken in the latest week.
The time taken to receive a test result after taking a test has increased between 30 July and 5 August compared to the previous week for all routes. The biggest increases were seen in home testing kits and satellite test centres, 43.6% of test results by these routes were received within 48 hours in the most recent week compared to 72.9% in the previous week. These increases are mainly due to an IT systems failure at one of the laboratories which resulted in a delay to the processing of results.
For all routes combined,[footnote 5] 50.6% of tests from all test sites were received within 24 hours of a test being taken in the latest week, and 76.7% by the next day. Excluding home testing kits, this was 60.3% of all tests and 86.5% by the next day.
Figure 5: percentage of results received within 24 hours (in-person tests) or within 48 hours (home/satellite tests), by route,[footnote 6] England
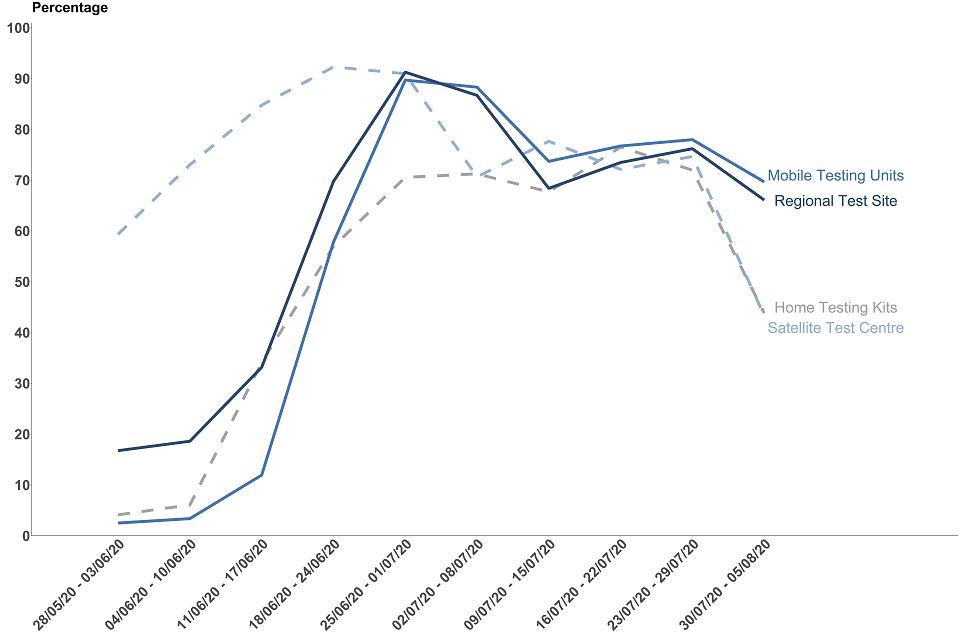
The data for the most recent weeks can be found in the annex, tables 3 to 3D
Regional test sites
In the most recent week, 66.1% of test results were received within 24 hours of the test being taken, compared to 76.2% in the previous week. If we consider the day the test was taken, 93.4% of tests results were received the next day.
Mobile testing units
In the most recent week, 69.6% of test results were received within 24 hours of the test being taken, compared to 78.0% in the previous week. If we consider the day the test was taken, 94.0% of tests results were received the next day.
Satellite test centres
Satellite tests are predominantly used by care homes who need greater control and flexibility over when test kits are collected. For example, tests may be conducted over multiple days with a collection scheduled a few days later. Because of this a lower proportion of test results will be available within 24 hours of the test being taken. In the most recent week, 43.3% of test results were received within 48 hours of the test being taken, compared to 74.6% in the previous week.
Home testing kits
Home tests take time to be posted to a person and be couriered back to the lab. Because of this a low proportion of test results will be available within 24 hours of the test being taken. In the most recent week, 43.8% of test results were received within 48 hours of the test being taken, compared to 72.0% in the previous week.
Contact tracing in England
Once a person has a confirmed positive test result for coronavirus,[footnote 7] this person is transferred to NHS Test and Trace and a case is opened for them. The number of positive cases transferred to the contact-tracing system may not always align with the number of people testing positive for COVID-19. There are several reasons for this which are outlined in the information for users document.
Positive cases transferred to NHS Test and Trace are handled in different ways depending on their complexity. Positive cases linked to potential outbreaks in specific settings are handled by PHE Local Health Protection Teams, these are termed complex cases, whereas those managed more generally by online and call centre capacity are termed non-complex cases. Further information is available in the NHS Test and Trace statistics methodology.
Positive cases transferred to NHS Test and Trace
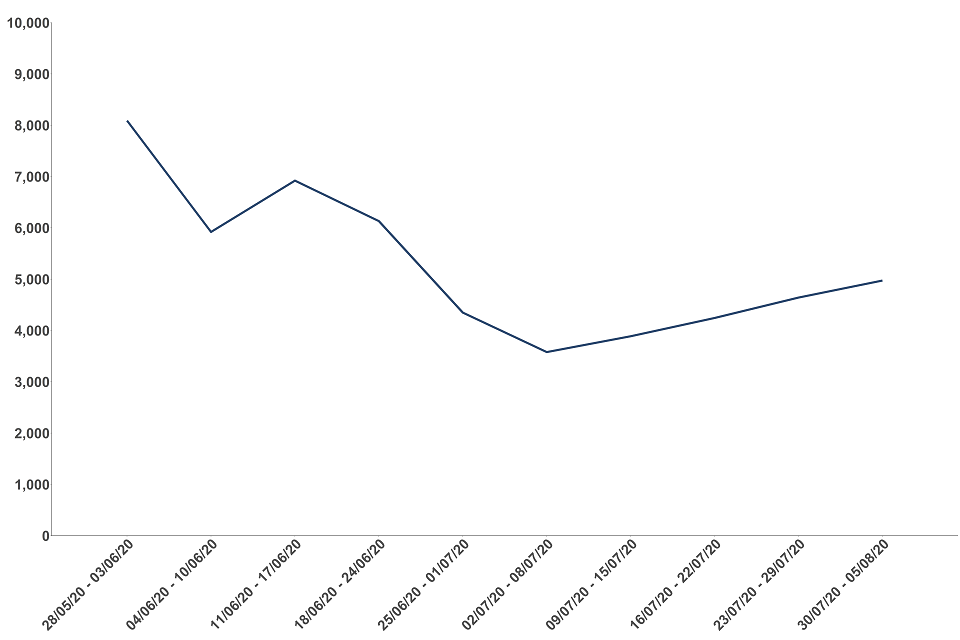
The number of people transferred to the contact-tracing system in the latest week has increased by 7% compared to the previous week, in line with the upward trend in people testing positive since the beginning of July
Between 30 July and 5 August, 4,973 people were transferred to the contract tracing system. This correlates with the number of people testing positive which has also been on the increase since the beginning of July. The number of people transferred is still 39% lower compared to when Test and Trace launched at the end of May due to the overall reduction in people testing positive for coronavirus (COVID-19).
Figure 6: number of people transferred to the contact-tracing system (includes complex and non-complex cases), England
Between 30 July and 5 August around 4 in every 5 people transferred to the contact-tracing system were reached and asked to provide information about their contacts
Out of the 4,973 people transferred to the contact-tracing system in the latest week, 3,962 (79.7%) were reached, 967 (19.4%) were not reached and 44 (0.9%) had no communication details. These proportions have remained broadly consistent since 18 June.
In the latest week, 291 people, who were reached and asked to provide details of close contacts, were classified as complex cases whereas 3,671 people were classified as non-complex. For more information on the different categories of cases and the outcomes of contact tracing see the terminology section.
Table 1: people transferred to the contact-tracing system (includes complex and non-complex cases) by whether they were reached and asked to provide contact details, England[footnote 8]
|
23 July to 29 July: number of people (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
Since Test and Trace launched. 28 May to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
People who were reached and asked to provide details of recent close contacts |
3,739 (80.5%) |
3,962 (79.7%) |
41,254 (78.2%) |
|
People classified as non-complex |
3,470 |
3,671 |
35,029 |
|
People classified as complex |
269 |
291 |
6,225 |
|
People who were not reached |
822 (17.7%) |
967 (19.4%) |
9,938 (18.8%) |
|
People whose communication details were not provided |
81 (1.7%) |
44 (0.9%) |
1,543 (2.9%) |
|
Total |
4,642 |
4,973 |
52,735 |
Proportion of people transferred to the contact-tracing system who were reached by upper tier local authority (UTLA)
Figure 7: percentage of cases reached and asked to provide details of recent close contacts by UTLA since Test and Trace began
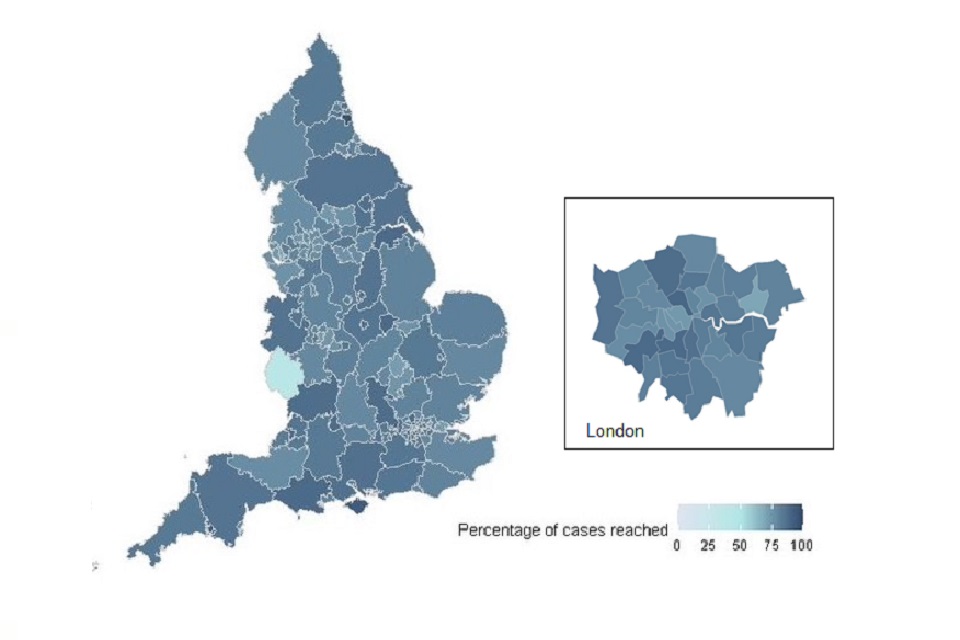
This data is available to download as a csv on the weekly publication collection page.
In the latest week around 4 in every 5 people who were reached and asked to provide information about their contacts, provided one or more close contacts
Out of the 3,962 people reached between 30 July and 5 August, 3,113 (78.6%) provided details of one or more close contacts. There has been a gradual increase in the proportion of people providing details for one or more close contacts since Test and Trace launched but remains broadly stable over the past 3 weeks
The number who were not able to give any recent close contacts refers to people who were successfully reached by NHS Test and Trace, but either had no recent close contacts or could not provide details of close recent contacts to pass on for further contact tracing (for example, recent close contact with strangers on the bus).
Figure 8: proportion of people transferred to the contact-tracing system (includes complex and non-complex cases) who were reached and asked to provide details of recent close contacts that provided details for one or more contact, England
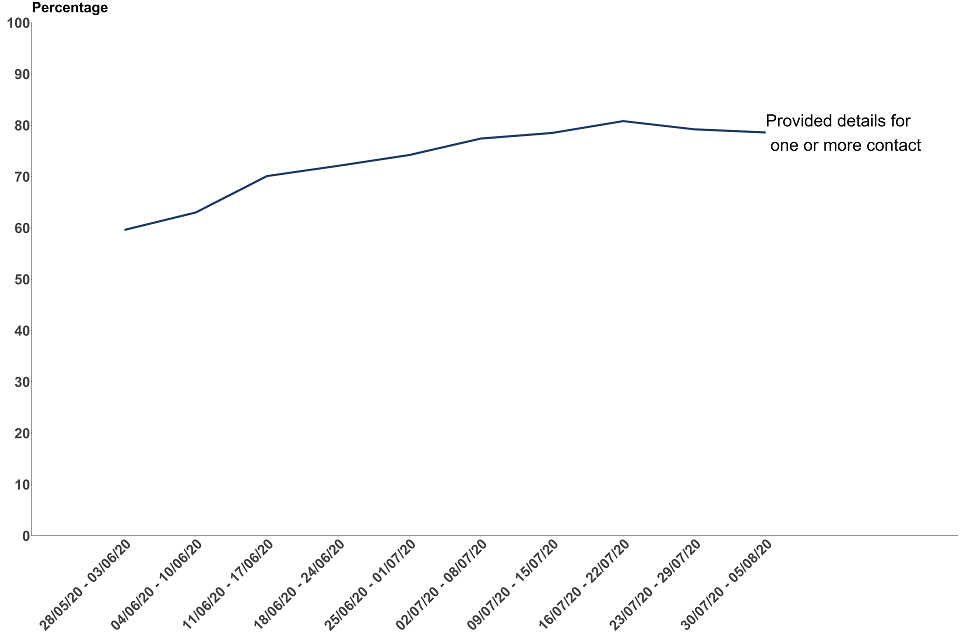
The data for the most recent weeks can be found in the annex, table 4.
For non-complex cases, most people continued to be successfully reached and asked to provide details about recent close contacts within 24 hours of their case being transferred to contact tracing
Between 30 July and 5 August, 71.8% of people (2,636) were reached within 24 hours in comparison to 73.1% in the previous week. Since Test and Trace launched on 28 May 25,607 (73.1%) of people have been reached within 24 hours.
Figure 9: proportion of people who were reached and asked to provide details about recent close contacts within 24 hours, England (excludes complex cases)
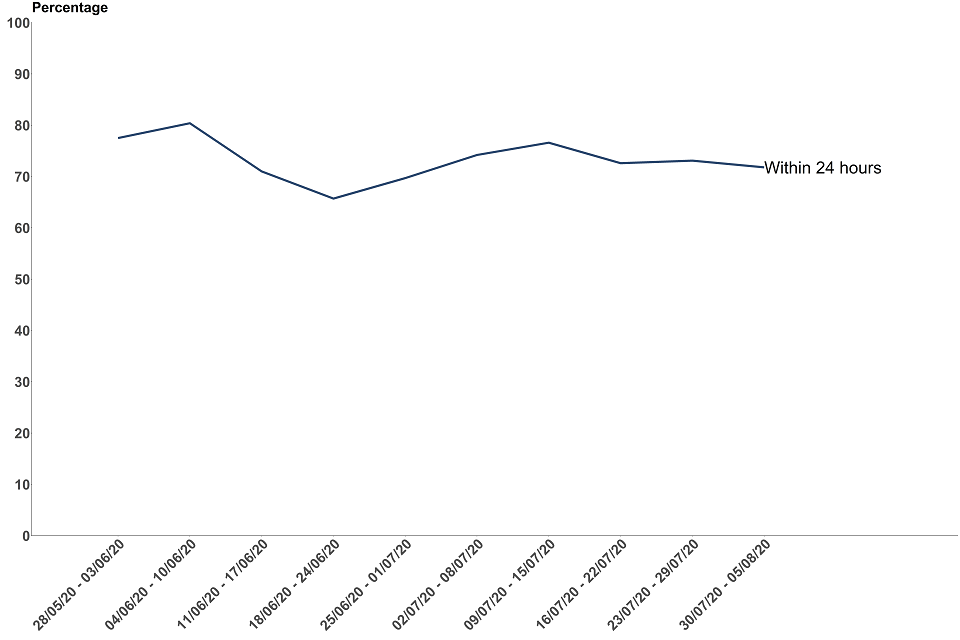
The data for the most recent weeks can be found in the annex, table 5.
Close contacts identified by NHS Test and Trace
The number of recent close contacts identified in the latest week has increased by 6% since the previous week but fallen by 61% since the start of contact tracing
Between 30 July and 5 August, 20,638 people were identified as recent close contacts, of which 12,731 were non-complex and 7,907 were complex. This has decreased by 61% since the start of contact tracing, comprised of an 82% decrease in the number of complex close contacts identified and 26% increase in the number of non-complex contacts.
As non-complex cases have a higher proportion of contacts who are unable to be reached, this has contributed to the reduction in the overall percentage of contacts who were reached and asked to self-isolate since Test and Trace launched, from 90.8% to 74.2% in the latest week.
Figure 10: number of people identified as recent close contacts, England
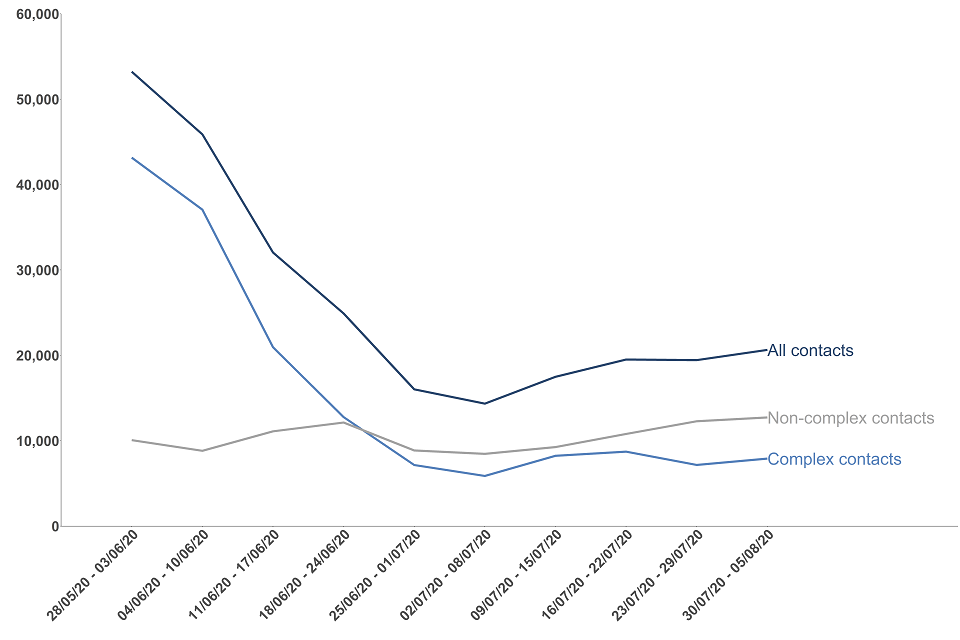
The data for the most recent weeks can be found in the annex, table 6.
The percentage of non-complex contacts who were reached and asked to self-isolate has increased from 52.5% to 61.1% since the start of Test and Trace
Between 30 July and 5 August, 12,731 non-complex close contacts were identified of which 7,780 (61.1%) were reached and asked to self-isolate. This percentage has seen an increase since the start of contact tracing and has remained constant for the last 4 weeks.
In the latest week, 2,671 (21.0%) people were not reached and 2,280 (17.9%) people had no communication details. For more information on the different outcomes of contact tracing see the terminology section.
Table 2: number of people identified as recent non-complex close contacts, England
|
23 July to 29 July: number of people (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
Since Test and Trace launched. 28 May to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Total number of non-complex close contacts |
12,279 |
12,731 |
104,516 |
|
Close contacts reached and asked to self-isolate |
7,479 (60.9%) |
7,780 (61.1%) |
59,308 (56.7%) |
|
Close contacts not reached |
2,470 (20.1%) |
2,671 (21.0%) |
22,915 (21.9%) |
|
Communication details not provided |
2,330 (19.0%) |
2,280 (17.9%) |
22,293 (21.3%) |
Proportion of non-complex close contacts identified who were reached and asked to self-isolate by upper tier local authority
Figure 11: percentage of non-complex contacts reached and asked to provide details of recent close contacts by UTLA since Test and Trace began
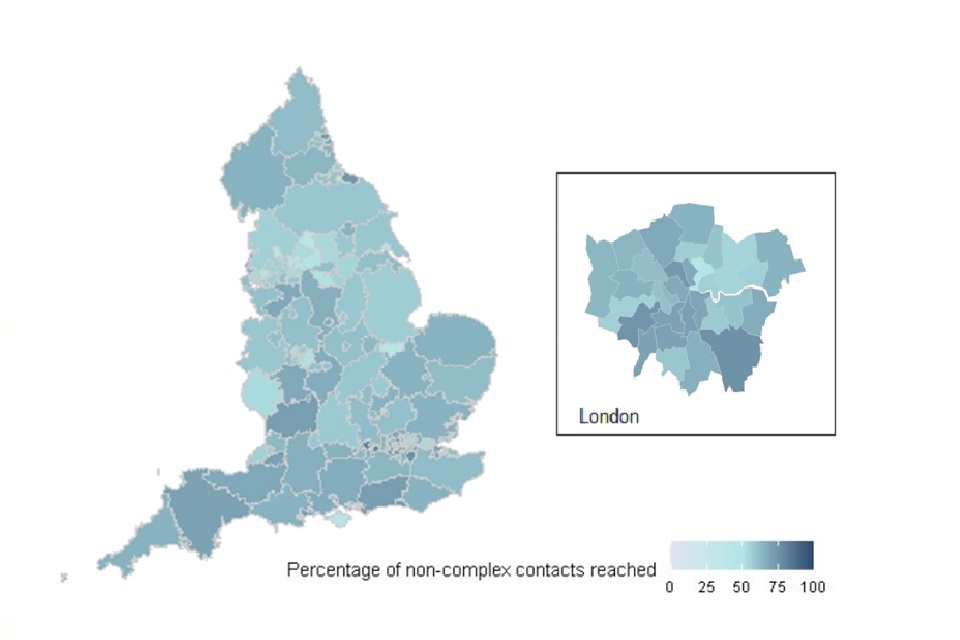
This data is available to download as a csv on the weekly publication collection page.
In the most recent week around 3 out of 5 non-complex contacts were from the same household as the case they were identified from
The proportion of non-complex close contacts from the same household as the case they were identified from has been steadily declining since Test and Trace launched. Between 30 July and 5 August, 61.8% of non-complex contacts were household contacts which remains the same as the previous week. In the same period, 57.4% of these household contacts were successfully reached and asked to self-isolate. This is in comparison to 67.1% for non-complex contacts who were from a different household to the case from which they were identified.
It is likely that cases often advise their household members to self-isolate in advance of these contacts being directly contacted by contact tracers. This results in these contacts not being recorded as reached and asked to self-isolate, which may be a contributing factor to a lower proportion of household contacts being reached in comparison to non-household contacts.
Figure 12: proportion of recent close non-complex contacts that were from the same household as the case that they were identified from, England
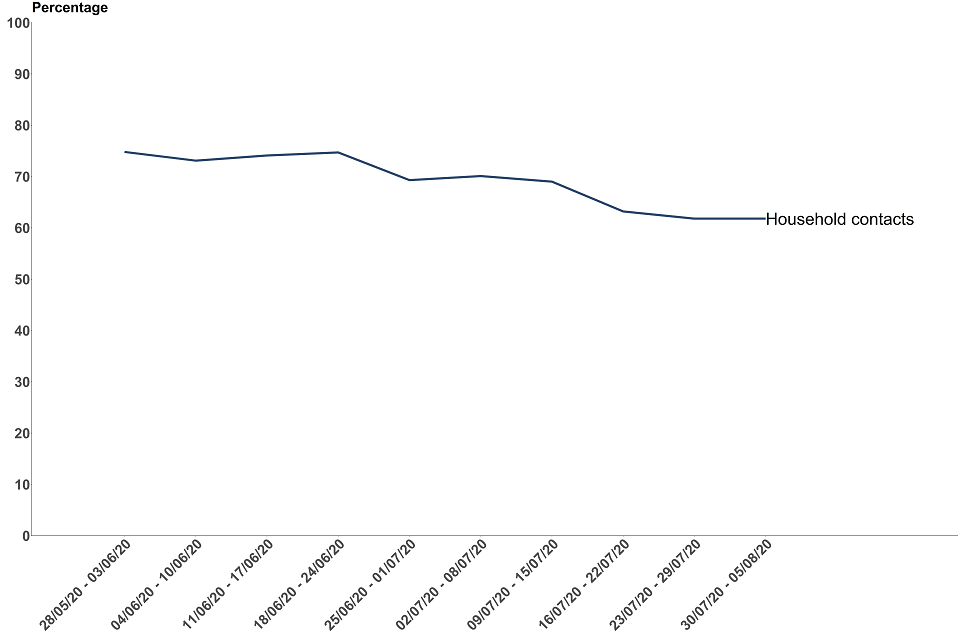
The data for the most recent weeks can be found in the annex, table 7.
For non-complex contacts who were advised to self-isolate, more than 4 out of 5 of them were reached within 24 hours of being identified[footnote 9]
Between 30 July and 5 August, 80.9% of non-complex contacts that were advised to self-isolate were reached within 24 hours of being identified. This has fallen slightly over the last 4 weeks, since 9 July. Since Test and Trace launched 82.5% of all non-complex contacts were reached and advised within 24 hours.
Table 3: people identified as recent close contacts who were advised to self-isolate by time taken to reach them England (excludes complex contacts)
|
23 July to 29 July: number of people (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
Since Test and Trace launched. 28 May to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Within 24 hours |
6,061 (81.1%) |
6,294 (80.9%) |
48,894 (82.5%) |
|
Between 24 and 48 hours |
1,134 (15.2%) |
1,202 (15.5%) |
8,022 (13.5%) |
|
Between 48 and 72 hours |
215 (2.9%) |
228 (2.9%) |
1,562 (2.6%) |
|
After 72 hours |
64 (0.9%) |
54 (0.7%) |
760 (1.3%) |
|
Total |
7,474 |
7,778 |
59,238 |
For non-complex contacts who were advised to self-isolate, over half were reached within 24 hours of the case that reported them being transferred to the contact-tracing system
Between 30 July and 5 August, 51.5% of non-complex contacts who were advised to self-isolate were reached within 24 hours of the case that reported them being transferred to the contact-tracing system. This has remained broadly consistent for the past 4 weeks.
This measure gives a sense of the end-to-end journey time through the Test and Trace system from when an individual testing positive was reported to NHS Test and Trace, to when their close contacts were reached and advised to self-isolate.
Figure 13: proportion of recent close contacts who were advised to self-isolate by time taken from the case that reports them being transferred to the contact-tracing system, England (excludes complex contacts)
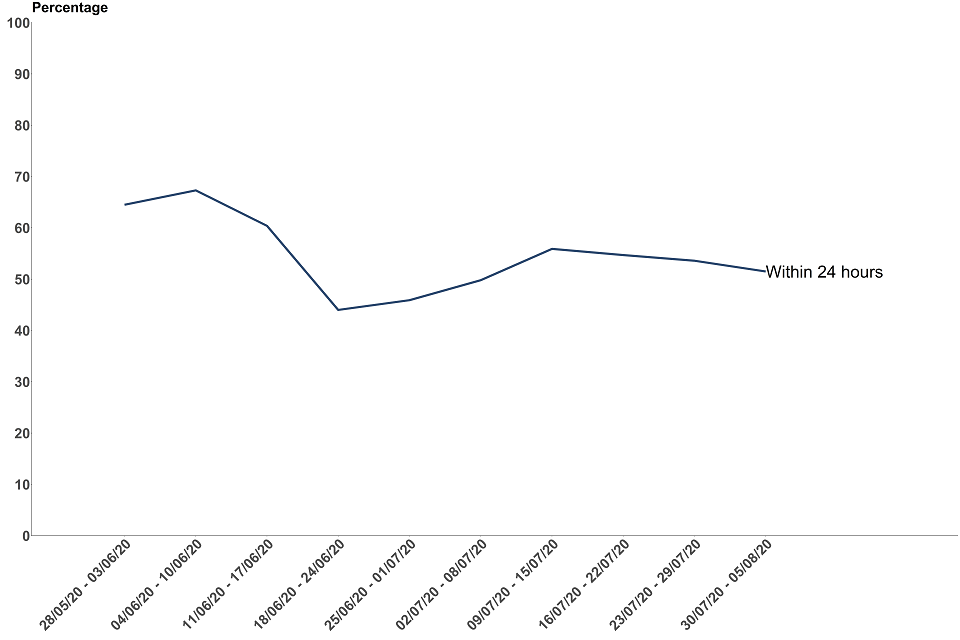
The data for the most recent weeks can be found in the annex, table 8.
Almost all complex contacts continue to be reached and asked to self-isolate
Between 30 July and 5 August, 7,907 complex close contacts were identified of which 7,528 (95.2%) were reached and asked to self-isolate and 379 (4.8%) were not reached. The proportion of complex close contacts successfully reached has increased slightly from 92.2% since the previous week. Since Test and Trace launched 97.9% of all complex contacts have been successfully reached.
Table 4: number of people identified as recent complex close contacts, England
|
23 July to 29 July: number of people (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
Since Test and Trace launched. 28 May to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Total number of complex close contacts identified |
7,165 |
7,907 |
158,999 |
|
Close contacts reached and asked to self-isolate |
6,608 (92.2%) |
7,528 (95.2%) |
155,582 (97.9%) |
|
Close contacts not reached |
557 (7.8%) |
379 (4.8%) |
3,417 (2.1%) |
Coronavirus (COVID-19) testing in the UK
From 13 August, statistics on coronavirus testing in the UK, across all 4 testing pillars are also included in this release. This includes details on laboratory testing capacity (lab capacity), number of tests sent out and number of tests processed since the start of testing in the UK. Definitions of the testing pillars can be found in the terminology section. Information about the government’s testing strategy testing can be found in Coronavirus (COVID-19): scaling up testing programmes.
A historic timeseries of weekly lab capacity, tests sent out and tests processed is available on the collection page for this release. Daily figures for tests processed and lab capacity are available on the PHE dashboard. Daily figures for all these measures are also available on the DHSC daily statistics page.
Testing capacity in the UK, pillars 1 to 4
Coronavirus tests are processed in several separate labs. Projected lab capacity is an estimate of each lab’s constrained capacity each day based on the staff, chemical reagents and other resources it has available. These estimates are made locally by the labs themselves. Further information on the methods for determining capacity is available in the COVID-19 testing data methodology note.
Testing capacity between 30 July to 5 August was 2,386,016 tests, an increase of 1.6% from the previous week.
Table 5: weekly lab testing capacity, pillars 1 to 4, UK[footnote 10]
|
23 July to 29 July: Lab Capacity |
30 July to 5 August: Lab Capacity |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Pillar 1 |
576,598 |
580,316 |
|
Pillar 2 |
882,500 |
890,000 |
|
Pillar 3 |
840,000 |
840,000 |
|
Pillar 4 |
48,700 |
75,700 |
|
UK total |
2,347,798 |
2,386,016 |
Number of tests sent out in the UK, pillar 2 and pillar 4
Tests can be administered in different ways – tests taken at a hospital, mobile testing unit, regional testing sites or tests sent out to individuals at home or satellite locations. Tests sent out are only available as part of pillar 2 (antigen testing) and pillar 4 (antigen and antibody testing). Not all tests sent out will be returned.
It is not currently possible to compare the total number of tests sent out with the total number of tests processed in pillar 2 and pillar 4, as given in Table 7. This is because tests sent out includes only tests sent to individuals at home or to satellite testing locations, while tests processed includes all tests that have remained within the control of the programme (and were counted at the time at which processed in labs) and those that have been sent out and subsequently returned to be processed in a lab. Further information is available in the COVID-19 testing data methodology note.
796,957 tests were sent out across the UK within pillars 2 and 4 between 30 July and 5 August of contact tracing. This has decreased by 8.7% since the previous week.
Table 6: number of tests sent out, pillars 2 and 4, UK
|
23 July to 29 July: number of Tests |
30 July to 5 August: number of Tests |
Total since data collection began |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Pillar 2 |
691,873 |
717,596 |
5,791,940 |
|
Pillar 4 |
181,015 |
79,361 |
920,022 |
|
UK total |
872,888 |
796,957 |
6,711,962 |
Number of tests processed in the UK, pillars 1 to 4
The number of tests processed counts all tests that have remained within the control of the programme (and were counted at the time at which processed in labs) and those that have been sent out and subsequently returned to be processed in a laboratory. They are counted at the time at which they were processed. This measure shows how many tests have been processed, including both antigen testing (pillar 1, pillar 2 and partial pillar 4) and antibody testing (pillars 3 and 4). Further details are available in the COVID-19 testing data methodology note.
For pillars 1 and 2, the number of tests processed in a laboratory is different to the number of test results received which is reported as part of the Test and Trace testing turnaround times for England. This is because they are reporting on the number of tests at different stages in the process as well as reporting different geographies (UK and England) and because some tests are excluded from the turnaround time counts.
Between 30 July and 5 August, 1,210,318 tests were processed in total across pillars 1 to 4, an increase of 25.1% since the previous week.
Table 7: number of tests processed, pillars 1 to 4, UK[footnote 10]
|
23 July to 29 July: number of Tests |
30 July to 5 August: number of tests |
Total since data collection began: number of tests |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Pillar 1 |
339,534 |
353,065 |
4,565,775 |
|
Pillar 2 |
518,470 |
610,413 |
5,517,652 |
|
Pillar 3 |
45,814 |
37,141 |
1,418,095 |
|
Pillar 4 |
63,553 |
209,699 |
1,070,469 |
|
UK total |
967,371 |
1,210,318 |
12,571,991 |
Terminology
Testing
Pillar 1 testing: swab (antigen) testing in Public Health England (PHE) labs, NHS hospitals for those with a clinical need, and health and care workers.
Pillar 2 testing: swab (antigen) testing for the wider population, through commercial partnerships,[footnote 11] carried out through several different routes:
-
regional test sites, which includes drive-through testing centres with limited walk-up facilities. This also includes Local Test Sites, which are similar to regional test sites but specifically for walk ups.
-
mobile testing units, which travel around the UK to increase access to COVID-19 testing. They respond to need, travelling to test people at specific sites including care homes, police stations and prisons.
-
satellite test centres, which includes test kits provided directly to ‘satellite’ centres at places like hospitals or care homes that have a particularly urgent or significant need.
-
home test kits, which are delivered to someone’s door so they can test themselves and their family without leaving the house.
Pillar 3 testing: serology testing to show if people have antibodies from having had coronavirus.
Pillar 4 testing: blood and swab testing for national surveillance support by PHE, ONS and research, academic and scientific partners to learn more about the prevalence and spread of the virus and for other testing research purposes.
People tested: refers to people who have newly been tested for COVID-19 and does not re-count people who have been tested more than once in either pillar 1 or pillar 2.
People testing positive: refers only to people who have newly tested positive for COVID-19 and does not include people who have had more than one positive test.
For pillar 2, there are 2 measures of the time taken to receive a coronavirus (COVID-19) test result:
-
The time taken to receive a COVID-19 test result from time of booking is measured from the time that a person books an appointment on the website to the time when the person receives a notification of their test result via an email or an SMS. This data is only available for regional test sites and mobile testing units, as test booking and registration processes for home testing and satellite test centres are currently undertaken on different systems.
-
The time taken to receive a COVID-19 test result from time of test is measured from the time a person completes a test registration (or the time a person indicates their test was taken for home testing kits) until the time that they receive a notification of the result of their test via an email or an SMS.
Tracing
NHS Test and Trace has 2 ways of handling cases depending on their complexity:
Complex cases and contacts - PHE Local Health Protection Teams manage cases linked to outbreaks, examples include someone who works or has recently visited:
-
a health or care setting, such as a hospital or care home
-
a prison or other secure setting
-
a school for people with special needs
-
critical national infrastructure or areas vital for national security
Non-complex cases and contacts - Wider online and other call centre capacity for less complex cases.
When a case is transferred to NHS Test and Trace contact tracers will attempt to contact the individual which results in one the following 3 outcomes:
-
Reached and provided information about recent close contacts – contact tracers successfully reached the individual and asked them to provide details for recent close contacts
-
No communication details provided - people who had no communication details provided are those who were transferred to NHS Test and Trace but did not have any associated contact details (e.g. phone number or email address).
-
Not reached - The number of people who were not reached includes those people who the service has been unable to reach because there has been no response to text, email and call reminders. It also includes people who were reached but declined to give details of close contacts. There may also be a small number of people who have not been reached but where contact tracers are still in the process of trying to make contact.
Measuring the data
How the data were collected
UK level testing data is collated centrally by DHSC from multiple sources across the different nations and pillars. Further details can be found in the COVID-19 testing data methodology note.
Testing data for pillars 1 and 2 for England are provided by PHE, NHS and commercial partners. Contact tracing data are collected from management information from the NHS Test and Trace service. Details about the data sources used can be found in the NHS Test and Trace statistics methodology document.
Future development
We have integrated these data with those from other parts of NHS Test and Trace, particularly testing, to provide an end-to-end view of the service that follows the user journey. So far, UK level testing data, testing data for pillars 1 and 2 in England and their turnaround times have been added. Further breakdowns for contact tracing continue to be incorporated, including complex and non-complex breakdowns, geographical breakdowns and household information.
To support user needs and data transparency, additional releases have been published alongside the weekly Test and Trace publication including care home statistics up to 8 July, people tested for coronavirus (COVID-19) between 30 January and 27 May and weekly UK testing statistics since the start of testing. NHS Test and Trace continues to provide information for local authorities and their partners so that they have the information they need to help contain any outbreaks.
In time, NHS Test and Trace intends to publish detailed data from across the program to support secondary analysis, for example in academic institutions. Over the coming months, we intend to make the following available:
Expected from August 2020:
- characteristics for those tested under pillar 2
- high-level UK test and trace figures
Expected from September 2020:
- details of close contacts who go on to test positive
The UK Statistical Authority has published a rapid review of the Test and Trace statistics. This includes recommendations on how the publication should develop it order to adhere fully to the Code of Practice. These recommendations continue to influence the development of the publication in the coming weeks and months.
Strengths and limitations
Given the importance of this service and the commitment of NHS Test and Trace to be open and transparent with the public it serves, these data are being released at the earliest possible opportunity. However, new IT systems and statistical outputs often take a period of time to bed in. These data should therefore be treated with caution as the system and understanding of the data develops.
Quality
These statistics have been put together by NHS Test and Trace and DHSC with advice from the Office for National Statistics.
More information on quality and how this publication adheres to the Code of Practice for statistics is available in the Statement of Compliance.
Feedback
For questions about the release please refer to the information for users document initially. For feedback and any further questions, please contact [email protected].
Annex A: tables
Annex table 1: people newly tested for COVID-19 under pillars 1 and 2, England
|
23 July to 29 July: number of people (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
Since Test and Trace launched. 28 May to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Pillar 1 |
131,910 |
137,052 |
1,217,070 |
|
Tested positive |
671 |
555 |
12,956 |
|
Pillar 2 |
259,877 |
301,352 |
2,312,118 |
|
Tested positive |
4,327 |
4,657 |
40,471 |
|
Total |
391,787 |
438,404 |
3,529,188 |
|
Tested positive |
4,998 |
5,212 |
53,427 |
Annex table 2: time taken from receipt of the test by a laboratory to the time the result is published, pillar 1, England
|
23 July to 29 July: number of tests (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of tests (percentage) |
9 July to 5 August: number of tests (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Total tests conducted in pillar 1 |
282,150 |
290,129 |
1,106,695 |
|
Number of tests completed within 24 hours turnaround |
257,070 (91.1%) |
255,838 (88.2%) |
989,907 (89.4%) |
|
Number of tests exceeding 24 hours turnaround |
25,080 (8.9%) |
34,291 (11.8%) |
116,788 (10.6%) |
Annex table 3: time from taking a test to receiving test results,[footnote 12] pillar 2 all routes, England
|
23 July to 29 July: number of tests (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of tests (percentage) |
28 May to 5 August: number of tests (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Within 24 hours |
180,141 (53.6%) |
188,278 (50.6%) |
1,118,460 (38.6%) |
|
Between 24 and 48 hours |
122,502 (36.4%) |
122,377 (32.9%) |
1,256,915 (43.3%) |
|
Between 48 and 72 hours |
23,624 (7.0%) |
28,617 (7.7%) |
380,571 (13.1%) |
|
After 72 hours |
7,842 (2.3%) |
29,503 (7.9%) |
123,227 (4.2%) |
|
Not completed |
2,127 (0.6%) |
3,682 (1.0%) |
20,336 (0.7%) |
|
Total |
336,236 |
372,457 |
2,899,509 |
Annex table 3a: time from taking a test to receiving test results, pillar 2 regional test sites, England
|
23 July to 29 July: number of tests (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of tests (percentage) |
28 May to 5 August: number of tests (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Within 24 hours |
100,991 (76.2%) |
114,350 (66.1%) |
643,019 (62.2%) |
|
Between 24 and 48 hours |
29,873 (22.5%) |
55,475 (32.1%) |
367,770 (35.6%) |
|
Between 48 and 72 hours |
472 (0.4%) |
1,153 (0.7%) |
10,380 (1.0%) |
|
After 72 hours |
240 (0.2%) |
229 (0.1%) |
3,699 (0.4%) |
|
Not completed |
989 (0.7%) |
1,844 (1.1%) |
8,827 (0.9%) |
|
Total |
132,565 |
173,051 |
1,033,695 |
Annex table 3b: time from taking a test to receiving test results, pillar 2 mobile testing units, England
|
23 July to 29 July: number of tests (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of tests (percentage) |
28 May to 5 August: number of tests (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Within 24 hours |
72,308 (78.0%) |
70,096 (69.6%) |
381,500 (59.0%) |
|
Between 24 and 48 hours |
18,584 (20.0%) |
27,640 (27.5%) |
240,235 (37.1%) |
|
Between 48 and 72 hours |
505 (0.5%) |
1,032 (1.0%) |
12,677 (2.0%) |
|
After 72 hours |
513 (0.6%) |
494 (0.5%) |
4,324 (0.7%) |
|
Not completed |
826 (0.9%) |
1,381 (1.4%) |
8,261 (1.3%) |
|
Total |
92,736 |
100,643 |
646,997 |
Annex table 3c: time from taking a test to receiving test results, pillar 2 satellite test centres,[footnote 13] England
|
23 July to 29 July: number of tests (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of tests (percentage) |
28 May to 5 August: number of tests (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Within 24 hours |
3,943 (10.1%) |
2,613 (7.2%) |
71,480 (13.8%) |
|
Between 24 and 48 hours |
25,330 (64.6%) |
13,100 (36.1%) |
304,388 (58.8%) |
|
Between 48 and 72 hours |
7,995 (20.4%) |
6,620 (18.2%) |
103,382 (20.0%) |
|
After 72 hours |
1,727 (4.4%) |
13,633 (37.6%) |
35,983 (7.0%) |
|
Not completed |
220 (0.6%) |
330 (0.9%) |
2,313 (0.4%) |
|
Total |
39,215 |
36,296 |
517,546 |
Annex table 3d: time from taking a test to receiving test results, pillar 2 home testing kits, England
|
23 July to 29 July: number of tests (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of tests (percentage) |
28 May to 5 August: number of tests (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Within 24 hours |
2,899 (4.0%) |
1,219 (2.0%) |
22,461 (3.2%) |
|
Between 24 and 48 hours |
48,715 (67.9%) |
26,162 (41.9%) |
344,522 (49.1%) |
|
Between 48 and 72 hours |
14,652 (20.4%) |
19,812 (31.7%) |
254,132 (36.2%) |
|
After 72 hours |
5,362 (7.5%) |
15,147 (24.2%) |
79,221 (11.3%) |
|
Not completed |
92 (0.1%) |
127 (0.2%) |
935 (0.1%) |
|
Total |
71,720 |
62,467 |
701,271 |
Annex table 4: people transferred to the contact-tracing system who were reached and asked to provide details of recent close contacts, by whether they provided details for contacts or not, England (includes both complex and non-complex cases)
|
23 July to 29 July: number of people (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
Since Test and Trace launched. 28 May to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
People who provided details of one or more close contacts |
2,960 (79.2%) |
3,113 (78.6%) |
29,723 (72.0%) |
|
People who were not able to give any recent close contacts |
779 (20.8%) |
849 (21.4%) |
11,531 (28.0%) |
|
Total |
3,739 |
3,962 |
41,254 |
Annex table 5: people who were reached and asked to provide details about recent close contacts by time taken from case being transferred, England (excludes complex cases)
|
23 July to 29 July: number of people (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
Since Test and Trace launched. 28 May to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Within 24 hours |
2,535 (73.1%) |
2,636 (71.8%) |
25,607 (73.1%) |
|
Between 24 and 48 hours |
710 (20.5%) |
736 (20.0%) |
6,498 (18.6%) |
|
Between 48 and 72 hours |
125 (3.6%) |
172 (4.7%) |
1,520 (4.3%) |
|
After 72 hours |
100 (2.9%) |
127 (3.5%) |
1,404 (4.0%) |
|
Total |
3,470 |
3,671 |
35,029 |
Annex table 6: number of people identified as recent close contacts by whether they were reached and asked to self-isolate, England (includes both complex and non-complex contacts)
|
23 July to 29 July: number of people (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
Since Test and Trace launched. 28 May to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Total number of close contacts identified |
19,444 |
20,638 |
263,515 |
|
Close contacts reached and asked to self-isolate |
14,087 (72.4%) |
15,308 (74.2%) |
214,890 (81.5%) |
|
Close contacts not reached |
5,357 (27.6%) |
5,330 (25.8%) |
48,625 (18.5%) |
Annex table 7: number of recent close non-complex contacts by whether they were from the same household as the case that they were identified from, England
|
23 July to 29 July: number of people (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
Since Test and Trace launched. 28 May to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Total number non-complex household contacts |
7,589 |
7,864 |
72,009 |
|
Close contacts reached and asked to self-isolate |
4,340 (57.2%) |
4,515 (57.4%) |
38,506 (53.5%) |
|
Close contacts not reached |
3,249 (42.8%) |
3,349 (42.6%) |
33,503 (46.5%) |
|
Total number non-complex not household contacts |
4,690 |
4,867 |
32,507 |
|
Close contacts reached and asked to self-isolate |
3,139 (66.9%) |
3,265 (67.1%) |
20,802 (64.0%) |
|
Close contacts not reached |
1,551 (33.1%) |
1,602 (32.9%) |
11,705 (36.0%) |
Annex table 8: number of close contacts who were advised to self-isolate by time taken from the case that reports them being transferred to the contact-tracing system England (excludes complex contacts[footnote 14])
|
23 July to 29 July: number of people (percentage) |
30 July to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
Since Test and Trace launched. 28 May to 5 August: number of people (percentage) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Within 24 hours |
3,971 (53.6%) |
3,988 (51.5%) |
32,032 (54.4%) |
|
Between 24 and 48 hours |
2,239 (30.2%) |
2,155 (27.8%) |
16,646 (28.3%) |
|
Between 48 and 72 hours |
807 (10.9%) |
861 (11.1%) |
5,996 (10.2%) |
|
After 72 hours |
388 (5.2%) |
746 (9.6%) |
4,176 (7.1%) |
|
Total |
7,405 |
7,750 |
58,850 |
-
For information on how people newly tested and newly testing positive is measured see the NHS Test and Trace statistics methodology. ↩
-
Includes a small number of people who had a test under pillar 4 (serology and swab testing for national surveillance). ↩
-
Note that these figures do not align with other published figures for people tested and people tested positive for COVID-19 under pillars 1 and 2. The reasons for this are outlined in the information for users document. ↩
-
For all measures of time taken to receive a COVID-19 test result, there are a number of tests that were not completed. This covers any test where the results were not communicated, which may be because communication details (for example, phone number or email address) were not provided or were incorrect, or because the test was cancelled or abandoned, or no result was available. ↩
-
All routes includes regional test sites (RTS), local test sites (LTS), mobile testing units (MTU), satellite test centres (STC) and home test kits (HTK). ↩
-
In person tests are those from regional Test Sites and mobile testing units. Home/satellite tests are those from satellite test centres and home testing kits. ↩
-
All positive test results under pillar 1 and pillar 2 should be transferred. In addition, all positive swab test results as part of prevalence studies (pillar 4) are also transferred to Test and Trace providing they did not test positive as part of an anonymous study. People tested under pillar 3 (serology testing to show if people have antibodies from having had COVID-19) do not have their cases transferred to NHS Test and Trace. ↩
-
If NHS Test and Trace is not able to reach an individual testing positive or if no communication details are available, then it is not always possible to know if the case is complex or non-complex. Therefore, these breakdowns are not available. ↩
-
Timing data does not include non-complex contacts which were subsequently escalated to complex. ↩
-
See more detail in Scaling up our testing programmes ↩
-
Please note the number of people receiving results within a given time is not the same as the number of people tested, because people may be tested more than once. ↩
-
This data does not include Randox tests, as these are handled through a different system. Randox tests make up a significant proportion of the tests conducted in care homes, which form part of the satellite test centres. ↩
-
This information is only available for non-complex contacts, although there are a small number of non-complex contacts where the time that their positive case was transferred is not available. ↩
