Prenatal pertussis vaccination coverage in England from January to March 2023 and annual coverage for 2022 to 2023
Updated 20 December 2024
Applies to England
Main points
This report evaluates prenatal pertussis vaccine coverage for women who delivered in the January to March 2023 quarter and estimates annual coverage for the 2022 to 2023 financial year.
The main findings were that:
-
vaccine coverage was 60.7% in the 2022 to 2023 financial year, compared to 64.7% in 2021 to 2022, 67.8% in 2020 to 2021 and 70.5% in 2019 to 2020
-
pertussis vaccine coverage in pregnant women for the fourth quarter 2022 to 2023 was 60.8%, which was 3.7 percentage points lower than the mean coverage for the same quarter in the 2021 to 2022 financial year
-
the mean coverage for the quarter was also 6.5 percentage points lower than the mean coverage for the same quarter in the 2020 to 2021 financial year
-
this observed decline in coverage has largely been driven by a decrease in London NHS Commissioning Region but is also reflected in other regions, particularly the North West and the Midlands
Background
This report presents pertussis vaccine coverage in pregnant women in England for the period January to March 2023, updating previous data reported for October to December 2022 (1). This report also includes annual coverage for the 2022 to 2023 financial year.
Following increased pertussis activity in all age groups, including infants under 3 months of age, and the declaration of a national pertussis outbreak in April 2012 (2), the pertussis vaccine has been offered to pregnant women since 1 October 2012 (3). The prenatal pertussis vaccination programme aims to minimise disease, hospitalisation and deaths in young infants, through the intra-uterine transfer of maternal antibodies, until they can be actively protected by the routine infant programme with the first dose of pertussis vaccine scheduled at 8 weeks of age (4).
In June 2014, the Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI) advised it should continue for a further 5 years (5). In February 2016, the JCVI considered new evidence demonstrating that vaccination earlier in pregnancy would increase opportunities during pregnancy for vaccination, without detrimentally affecting the protection afforded to the infant (6, 7). Based on this, JCVI advised that vaccination could be offered from gestational week 16, although for operational reasons vaccination should ideally be offered from around 20 weeks, on or after the foetal anomaly scan (8).
This advice was implemented from April 2016 as was offering the vaccine through general practice as well as some maternity services. In 2019, following the JCVI recommendation, the prenatal pertussis vaccine became a routine programme in England (9).
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, nationwide social distancing measures were initiated from 23 March 2020. To minimise disruptions, guidance to continue routine vaccination programmes – with priority given to time sensitive vaccines, such as for prenatal pertussis – were outlined by NHS England at the beginning of the pandemic (10).
In addition, the Royal College of Nursing published guidance on the management of immunisation clinics, and the then Public Health England (PHE) produced resources promoting immunisations to pregnant women and young families (11, 12).
Methods
GP level pertussis vaccine coverage data is automatically uploaded via participating GP IT suppliers to the ImmForm website each month. ImmForm data is validated and analysed by the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) to check data completeness, identify and query any anomalous data and describe epidemiological trends. Since April and May 2016 (implementation date varied by GP IT supplier), the following monthly data has been collected:
- denominator: number of women who delivered in the survey month, excluding miscarriages and stillbirths, regardless of gestational age
- numerator: number of women receiving pertussis vaccination between week 16 of pregnancy and delivery
For accurate denominators to be extracted from GP IT systems by the automated survey and precise coverage estimates to be calculated, it is important that the medical records of all women who have given birth have the following fields completed:
- the date of delivery
- the date of receipt of a pertussis-containing vaccine at or after week 16 of pregnancy, regardless of the setting where the vaccine was administered
- where relevant, fields indicating stillbirth or miscarriage
Coverage by former local teams and NHS commissioning regions (based on the 2019 NHS England configurations) is also included, for comparison, in the data tables associated with this report.
Clinical commissioning groups (CCGs) have been omitted due to changes in NHS geographies over time and the abolition of CCGs from 1 July 2022.
Annual vaccine coverage for England was calculated by summing the 12 monthly numerators and denominators for the financial year (April 2022 to March 2023). This is different from reports showing annual data on and prior to the 2018 to 2019 financial year, where a separate annual extraction (based on the same coding specification) was used to report the annual coverage.
Participation and data quality
All GP IT suppliers provided data for the January to March 2023 period. National GP practice participation was at 97.4% (January 2023), 98.0% (February 2023) and 97.9% (March 2023).
Results
Monthly pertussis vaccine coverage ranged across the quarter from 59.3% in March to 60.8% in January, with mean coverage for the quarter at 60.2% (Table 1, Figure 1), see data tables. During this quarter, prenatal pertussis vaccine coverage by Integrated Care Board (ICB) ranged from 28.0% (North Central London, March 2023) to 78.1% (Norfolk and Waveney, March 2023) (Table 1).
When compared with data from the 2021 to 2022 financial year, national coverage was 3.5 percentage points lower in January, 3.7 percentage points lower in February and 4.1 percentage points lower in March. Mean coverage for this quarter was 3.7 percentage points lower compared to national coverage reported for the same quarter in the 2021 to 2022 financial year, and 6.5 percentage points lower than the same period in the 2020 to 2021 financial year, representing an ongoing decline in coverage since June 2020 (Figure 1).
Coverage in quarter 4 (January to March 2023) was the lowest measured since April 2016 when the new IT specification was implemented (Figure 1) (13).
The annual vaccine coverage for the 2022 to 2023 financial year was 60.7%. This is 4 percentage points lower than the 2021 to 2022 financial year and 7.1 percentage points lower than the 2020 to 2021 financial year.
Coverage by former local teams and NHS commissioning regions (based on the 2019 NHS England configurations) are also included in the data tables associated with this report, for trend comparisons.
In the London NHS commissioning region there was a steep decline in coverage after December 2019. Coverage in London decreased by 23.3 percentage points between December 2019, when coverage was 60.9%, and June 2022, when coverage was 37.6% (Figure 2); coverage stabilised from June 2022 to March 2023, albeit at a level considerably lower than other regions.
Table 1. Monthly pertussis vaccination coverage (%) in pregnant women by ICB in England, January to March 2023
| ICB code | ICB name | October 2022 | November 2022 | December 2022 | January to March 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QE1 | Lancashire and South Cumbria | 59.3 | 59.6 | 54.8 | 57.9 |
| QF7 | South Yorkshire | 68.4 | 69.7 | 68.7 | 68.9 |
| QGH | Herefordshire and Worcestershire | 65.6 | 69.1 | 67.3 | 67.3 |
| QH8 | Mid and South Essex | 64.8 | 64.9 | 61.6 | 63.7 |
| QHG | Bedfordshire, Luton, and Milton Keynes | 59.6 | 57.7 | 61.8 | 59.9 |
| QHL | Birmingham and Solihull | 45.4 | 46.4 | 42.7 | 44.8 |
| QHM | North East and North Cumbria | 64.5 | 63 | 60 | 62.6 |
| QJ2 | Derby and Derbyshire | 77.7 | 74.3 | 73.5 | 75.2 |
| QJG | Suffolk and North East Essex | 66.5 | 62.6 | 68.4 | 65.9 |
| QJK | Devon | 71.4 | 66.9 | 67.6 | 68.7 |
| QJM | Lincolnshire | 67 | 67.6 | 67.1 | 67.2 |
| QK1 | Leicester, Leicestershire and Rutland | 57.7 | 55.4 | 53.8 | 55.6 |
| QKK | South East London | 48.4 | 52 | 47.3 | 49.2 |
| QKS | Kent and Medway | 66.6 | 63.6 | 64.8 | 65 |
| QM7 | Hertfordshire and West Essex | 62.8 | 62.6 | 66.1 | 63.9 |
| QMF | North East London | 34.3 | 30.8 | 31.2 | 32.1 |
| QMJ | North Central London | 29.5 | 30.2 | 28 | 29.2 |
| QMM | Norfolk and Waveney | 75.8 | 74.3 | 78.1 | 76.1 |
| QNC | Staffordshire and Stoke-on-Trent | 58.2 | 54.8 | 54.5 | 55.9 |
| QNQ | Frimley | 64.2 | 57.1 | 56.3 | 59.1 |
| QNX | Sussex | 67.8 | 70.9 | 70.7 | 69.8 |
| QOC | Shropshire, Telford and Wrekin | 72.1 | 72.5 | 73.6 | 72.7 |
| QOP | Greater Manchester | 52.4 | 51.5 | 49.3 | 51.1 |
| QOQ | Humber and North Yorkshire | 72.8 | 72.6 | 70.7 | 72 |
| QOX | Bath and North East Somerset, Swindon and Wiltshire | 70.3 | 73.4 | 70.2 | 71.2 |
| QPM | Northamptonshire | 55.3 | 55.6 | 52.3 | 54.3 |
| QR1 | Gloucestershire | 65 | 70.2 | 63.9 | 66.3 |
| QRL | Hampshire and Isle of Wight | 72.5 | 72.2 | 70.1 | 71.6 |
| QRV | North West London | 39.4 | 42.1 | 40.8 | 40.7 |
| QSL | Somerset | 74.8 | 70.4 | 72.3 | 72.7 |
| QT1 | Nottingham and Nottinghamshire | 65.8 | 66.8 | 62.7 | 65 |
| QT6 | Cornwall and Isles of Scilly | 55.1 | 67.8 | 67.6 | 63.7 |
| QU9 | Buckinghamshire, Oxfordshire, and Berkshire West | 72.8 | 72.5 | 68.9 | 71.4 |
| QUA | Black Country | 49.4 | 50.8 | 49.6 | 49.9 |
| QUE | Cambridgeshire and Peterborough | 64.6 | 63.2 | 61 | 62.9 |
| QUY | Bristol, North Somerset, and South Gloucestershire | 72.8 | 70.6 | 73.5 | 72.4 |
| QVV | Dorset | 76 | 70.8 | 71.2 | 72.8 |
| QWE | South West London | 49.6 | 55.8 | 51.1 | 52.1 |
| QWO | West Yorkshire | 67.4 | 66.7 | 64.8 | 66.3 |
| QWU | Coventry and Warwickshire | 62.7 | 61.7 | 60.2 | 61.5 |
| QXU | Surrey Heartlands | 69.3 | 74.3 | 69.6 | 71 |
| QYG | Cheshire and Merseyside | 58.9 | 56.8 | 54.7 | 56.8 |
| Total | 60.8 | 60.5 | 59.3 | 60.2 |
Figure 1. Monthly pertussis vaccination coverage (%) in pregnant women (England), 2016 to 2023
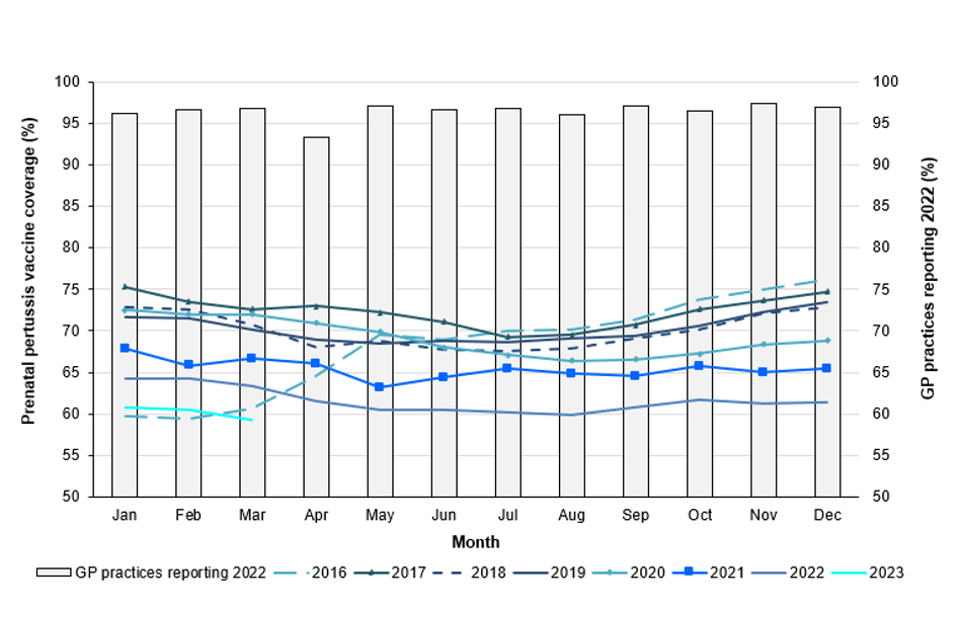
Figure 2. Monthly pertussis vaccination coverage (%) in pregnant women by NHS commissioning region, April 2019 to March 2023 [Note 1]

[Note 1] Data from the smallest IT supplier was excluded between November to December 2019.
Discussion
The number of confirmed cases in infants under 3 months, who are targeted by the maternal immunisation programme, continues to remain extremely low with 0 confirmed cases between July and September 2022 compared to 0, 1 and 29 cases in the same quarters in 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively (14). It continues to be important to encourage women to be immunised against pertussis at the optimal time during pregnancy in order to protect their babies from birth as levels of disease are likely to increase following the lifting of COVID-19 control measures.
This report evaluates pertussis vaccine coverage data for women who delivered in the period January to March 2023 (fourth quarter coverage) and between 1 April 2022 and 31 March 2023 (annual coverage for the financial year).
Overall, monthly prenatal pertussis vaccine coverage in the fourth quarter of financial year 2022 to 2023 went from 60.8% in January to 60.5% in February, and to 46.9% in March 2023. For the January to March 2023 quarter, the difference in mean coverage between the highest and lowest ICB was 46.9 percentage points.
For the whole of financial year 2022 to 2023, vaccine coverage was 60.7%, compared to 64.7% in 2021 to 2022, 67.8% in 2020 to 2021 and 70.5% in 2019 to 2020 – an almost 10% decline in a 4 year period.
Coverage in the London NHS commissioning region declined substantially after December 2019, falling 23.3 percentage points to June 2022. Sharing learning across the country, including those measures that have been successful in mitigating the impact of social distancing, may help address any gaps in coverage for future cohorts of pregnant women.
Limitations to the data presented in this report may explain the observed variability in coverage at the local level and over time. First, completeness of data is reliant on the recording of delivery dates in the mother’s medical records and a recent study in England suggests that maternity notes regarding pregnancy and delivery are often scanned or archived, rather than coded in an extractable format (15). Furthermore, a comparison of this denominator data with national data on live births (16) indicates that, in 2021, this data represented about 71% of the population of pregnant women.
Continued support in the delivery of this important programme has been sought from:
- service providers (GP practices and maternity units)
- screening and immunisation teams
- health protection teams (HPTs)
Screening and immunisation teams and HPTs should continue to update service providers on the current epidemiology of the disease and the need to maintain and improve coverage achieved thus far.
If coverage, and ultimately the impact of the programme itself, is to be accurately monitored, it is essential that GPs and practice nurses continue to ensure that vaccination and date of delivery are recorded in the patient’s GP record. In areas that have commissioned maternity units to offer pertussis vaccines in pregnancy, it is important that providers ensure doses of vaccines given to individual women are also communicated to the woman’s GP. Maternity units not offering pertussis vaccines to pregnant women should continue to discuss its importance, make use of available resources (17), and signpost women to their GP to receive the vaccine.
GPs, practice nurses, obstetricians, and midwives should continue to encourage pregnant women to receive the pertussis vaccine – ideally between weeks 20 and 32 of their pregnancy (but up to term) – so as to optimise protection for their babies from birth (8).
References
1. UKHSA (2022). Prenatal pertussis vaccination coverage in England from October to December 2022. Health Protection Report: volume 17, number 5
2. A level 3 incident is the third of 5 levels of alert under the PHE’s Incident Reporting and Information System (IERP) according to which public health threats are classified and information flow to the relevant outbreak control team is coordinated. A level 3 incident is defined as one where the public health impact is significant across regional boundaries or nationally. An IERP level 3 incident was declared in April 2012 in response to the ongoing increased pertussis activity.
3. DHSC (2012). Pregnant women to be offered whooping cough vaccination
4. UKHSA (2018). ‘Complete routine immunisation schedule’
5. JCVI (2014). Minute of the meeting on 4 June 2014
6. Eberhardt CS, Blanchard-Rohner G, Lemaitre B, Boukrid M, Combescure C, Othenin-Girard V and others (2016). ‘Maternal immunization earlier in pregnancy maximizes antibody transfer and expected infant seropositivity against pertussis’. Clinical Infectious Diseases: volume 62, pages 829 to 836
7. JCVI (2016). Minute of the meeting on 3 February 2016
8. UKHSA (2016). The Green Book, chapter 24: Pertussis
9. JCVI (2019). Minute of the meeting on 5 June 2019
10. NHS England (2020). Preparedness letter for general practice: 14 April 2020
11. Royal College of Nursing (2020). Immunisation
12. PHE (2020). Vaccine update: World Immunisation Week
13. PHE (2016). Pertussis vaccination programme for pregnant women: vaccine coverage estimates in England, April 2016 to September 2016.’ Health Protection Report: volume 10 number 41
14. UKHSA (2023). ‘Laboratory confirmed cases of pertussis in England: April to June 2022.’ Health Protection Report: volume 17 number 3
15. Llamas A, Amirthalingam G, Andrews N, and Edelstein M (2020). ‘Delivering prenatal pertussis vaccine through maternity services in England: what is the impact on vaccine coverage?’ Vaccine: volume 38, issue 33, pages 5,332 to 5,336
16. Office for National Statistics (2022). Provisional births in England and Wales
17. UKHSA (2022). Pregnancy: How to help protect you and your baby
