Abortion statistics for England and Wales during the COVID-19 pandemic
Updated 17 March 2021
Applies to England and Wales
This publication has been revised to emphasise that the statistics are provisional and subject to revision in the forthcoming ‘Abortion statistics for England and Wales: 2020’ National Statistics publication on 10 June 2021.
They have been produced as early figures and will be subject to further quality assurance before they are published as regular National Statistics.
They have been released as provisional to provide potential users with useful information, while stating clearly their nature and limitations. No changes have been made to the tables and figures in this revision.
1. Background
This report provides provisional statistics on abortions recorded in England and Wales from January to June 2020. It provides statistics for gestation (in weeks) and method of termination by month, to provide information on trends since the start of 2020 and the coronavirus pandemic. Monthly figures from January to June 2019 have been included for comparison purposes.
The data in this report should be treated as provisional due to the initial short time period between publication and the time period covered. Revised finalised figures will be published in the annual abortion publication on 10 June 2021.
Different methods can be used to terminate a pregnancy, depending on the gestation, and other circumstances relating to the individual woman. There are medical methods which involve the use of drugs (for example, mifepristone) and there are surgical methods, such as vacuum aspiration or dilatation and evacuation. (See glossary and guide to abortion statistics).
Early medical abortions (EMA) are defined as taking place within the first 10 weeks of pregnancy using medical methods. There are 2 stages to medical abortions, defined by the administering of 2 medications, antiprogesterone and prostaglandin.
From 30 March 2020, the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care put in place a temporary measure to limit the transmission of COVID-19 and ensure continued access to abortion services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eligible women and girls are able to take both pills for early medical abortion up to 10 weeks in their own homes, following a telephone or e-consultation with a clinician, without the need to first attend a hospital or clinic. This change has been made on a temporary basis only and is time limited for two years, or until the pandemic is over. The government has committed to undertake a public consultation on whether to make this measure permanent. This additional statistical release aims to inform this public consultation. This release also provides provisional statistics so that service providers are able to manage and plan service provision given the recent changes.
Since the end of 2018 in England, and since June 2018 in Wales, women have been allowed to administer the second stage of treatment for early medical abortions at home. Prior to this both stages could only be administered at a licenced NHS hospital or independent sector abortion clinic.
The information presented is based on abortion notification forms (HSA4) submitted by clinics and hospitals to the Chief Medical Officer (CMO) at the Department of Health & Social Care (DHSC). DHSC monitor the forms to ensure that there is full compliance with the legislation set out in the Abortion Act, 1967.
1.1 Further information
Further details on the legislative context of the Abortion Act, in addition to methodological and technical information on the data can be found in the ‘Guide to Abortion Statistics’, in Abortion statistics for England and Wales: 2019.
1.2 Previous publications
The Department of Health and Social Care (DHSC) has published abortion statistics annually since 2002. Statistics for years from 1974 to 2001 were published by the Office for National Statistics (ONS) in their Abortion Statistics Series AB, Nos 1 to 28. The reports for 1991 to 2001 are available electronically on request to [email protected]. Statistics for years from 1968 to 1973 were published in the Registrar General’s Statistical Review of England and Wales, Supplement on Abortion.
The most recent versions of the publication are available on GOV.UK.
Contact us at [email protected].
Abortion statistics are usually published annually. Currently, the next planned date of publication is 10 June 2021, and will cover January to December 2020.
2. Commentary
Unless specified, the following commentary, charts and tables are provisional and relate only to abortions in England and Wales between January to June 2020, for residents of England and Wales.
2.1 Overall number
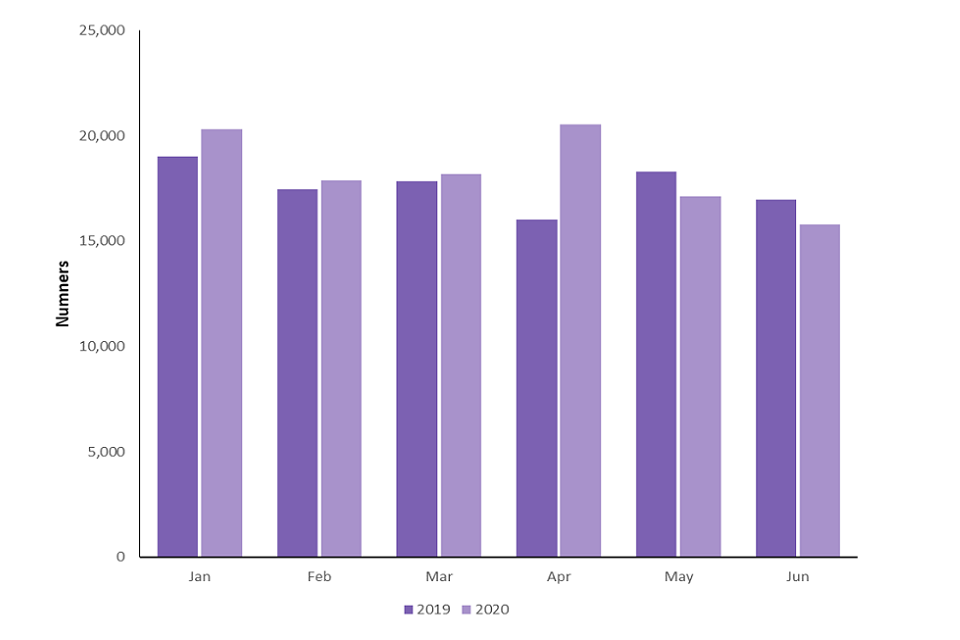
Between January to June 2020, there were 109,836 abortions performed on residents of England and Wales. This compares with 105,540 over the same period in 2019. For every month between January to April of 2020, there were more abortions performed compared with the corresponding month of 2019. In April 2020 there were just over 4,500 more abortions compared with April 2019. In May and June 2020, the number of abortions performed was less than the corresponding month in 2019 (figure 1 and table 1).
Figure 1: Number of abortions performed by month, resident of England and Wales, January to June 2019 and 2020
2.2 Gestation period
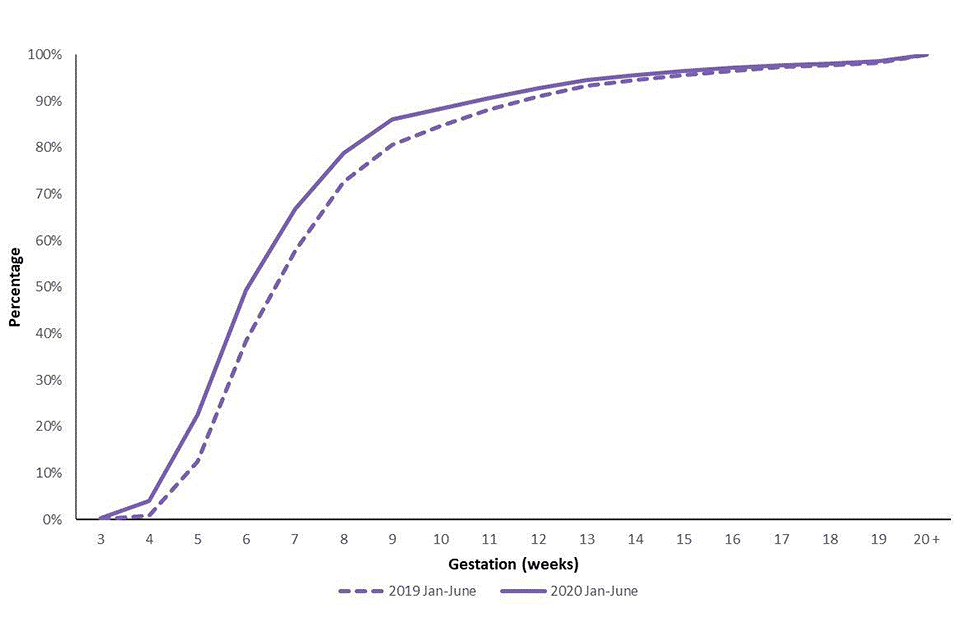
From January to June 2020, 86% of abortions were performed at under 10 weeks. This compares with 81% in January to June 2019, an increase of 5 percentage points.
Almost 50% of abortions were performed before 7 weeks gestation from January to June 2020, compared to almost 40% for the same period in 2019. A further 36% were done from weeks 7 to 9 in the first 6 months of 2020, compared to 42% in the first 6 months of 2019 (figure 2 and table 1).
Figure 2: Cumulative percentage of abortions performed by gestation, January to June 2019 and 2020 in England and Wales, residents of England and Wales
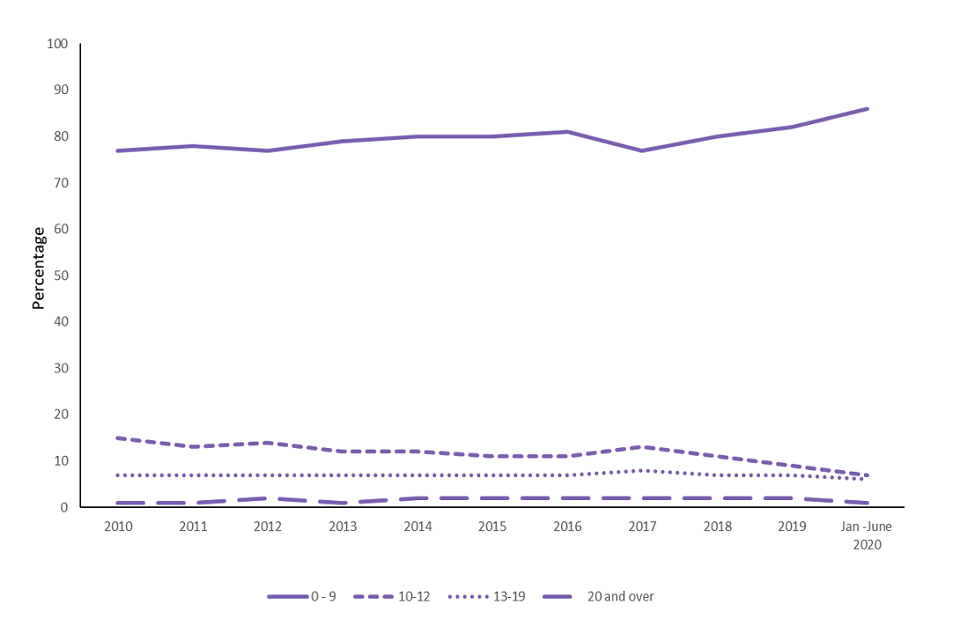
The proportion of abortions performed at under 10 weeks has gradually been increasing since 2010, when it was 77%. Over the whole 2019 calendar year, 82% of abortions were performed at under 10 weeks (figure 3 and table 3).
Figure 3: Percentage of abortions performed by gestation, 2010 to January to June 2020, residents of England and Wales
2.3 Method of abortion
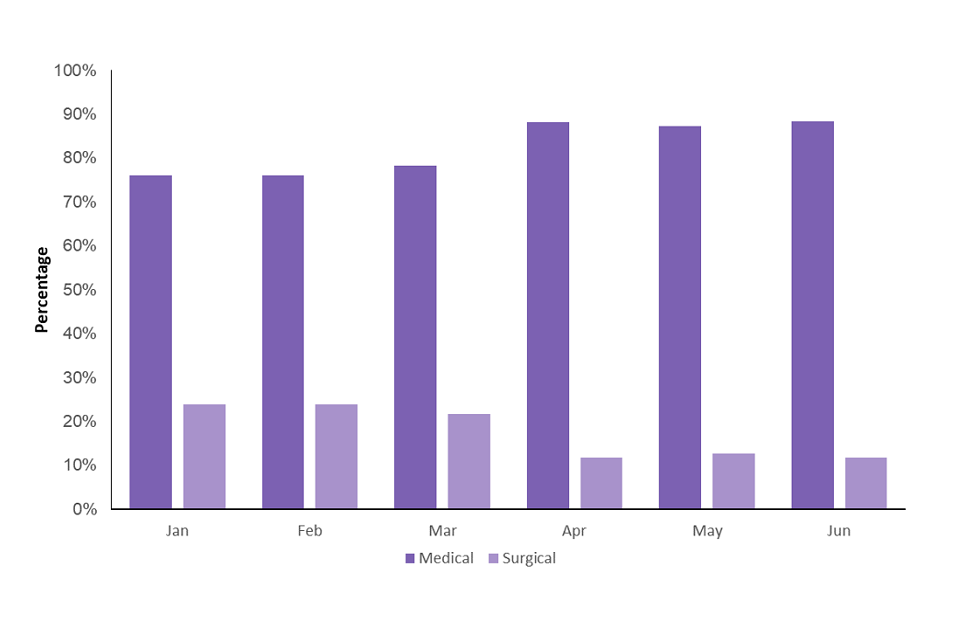
From January to June 2020, medical abortions accounted for 82% of abortions. This compares with 72% of abortions over the same period in 2019, and 73% of abortions over the full 2019 calendar year. The majority (96%) of medical abortions in the first 6 months of 2020 were performed at under 10 weeks, similar to the proportion in the first 6 months of 2019 (95%).
In March 2020, 78% of abortions were medical and 22% were surgical, whilst in April 2020, this changed to 88% of abortions being medical and 12% being surgical. This is likely to be a result of the temporary approval of women’s homes and the homes of registered medical practitioners as classes of place for early medical abortion up to 10 weeks. This increase follows a gradual continued upward trend in medical abortions since 1991, when mifepristone was first licensed for use in the UK (Table 3).
Figure 4: Percentage of abortions performed by method, January to June 2020 in England and Wales, residents of England and Wales
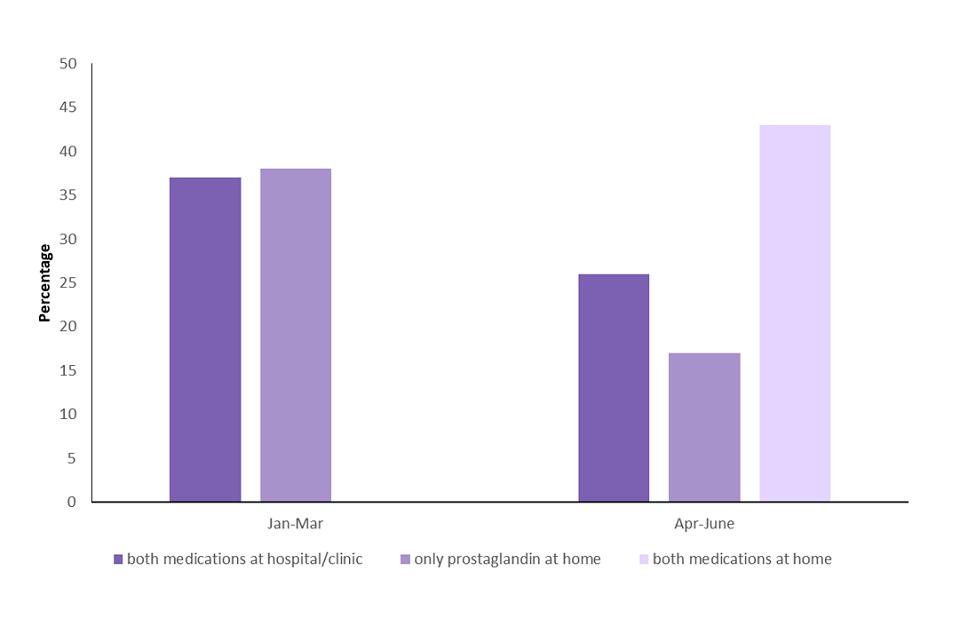
Between April and June 2020, there were 23,061 medical abortions where both medicines (antiprogesterone and prostaglandin) were administered at home, this represents 43% of abortions during this time. The percentage of abortions using this method increased between April and June, accounting for 33% of abortions in April and increasing to 51% of abortions in June (figure 5 and table 2).
Figure 5: Percentage of all abortions performed by medical method, January to March (Q1) and April to June (Q2) 2020 in England and Wales, residents of England and Wales
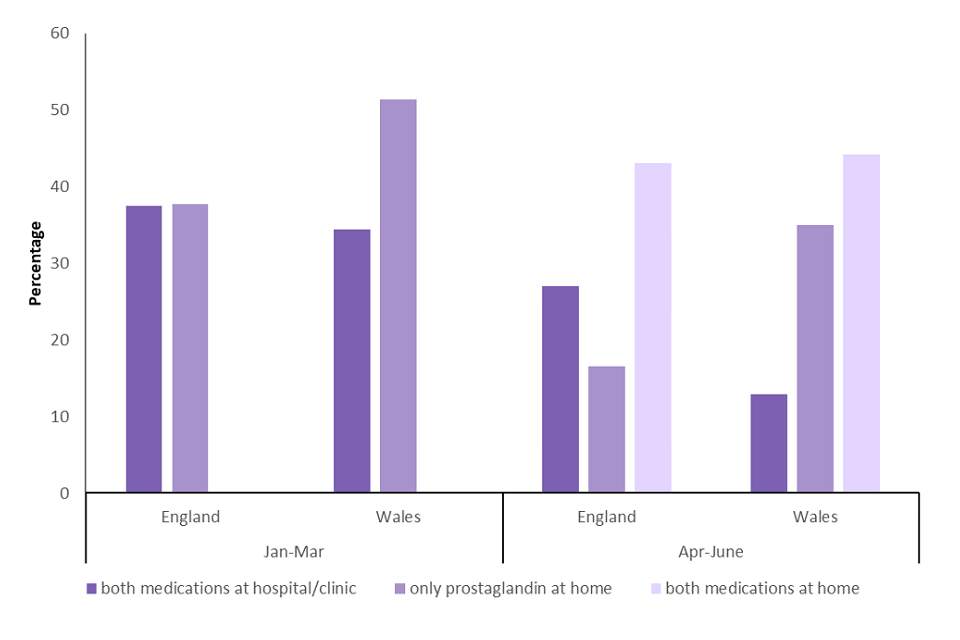
In 2019 and prior to the change introduced on the 30 March 2020, Wales had a higher proportion of abortions where only prostaglandin was taken at home, compared with England. This is likely a result of women being allowed to administer the second stage (prostaglandin) of early medical abortion at home in Wales from June 2018, while this change was introduced in England in late December 2018 (figure 6).
Between April and June 2020, England and Wales had a similar proportion of abortions where both stages of the early medical abortion were taken at home. England had a higher percentage of abortions where both stages were administered at an NHS hospital or licenced independent sector abortion clinic (27% in England compared with 13% in Wales). Wales had a higher proportion of abortions where just the second stage was administered at home (35% in Wales, 17% in England).
Figure 6: Percentage of abortions performed by medical method and country of residence, January to March (Q1) and April to June (Q2) 2020, residents of England and Wales
3. Glossary
|
Term |
Definition |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Chief Medical Officer (CMO) |
The CMO is the most senior government advisor on health matters in the UK. The CMO advises government on public health issues. This extends to recommending policy changes affecting the law governing abortion and advising doctors who perform abortions, regarding the interpretation of that law. There are four in total, each one advising either Her Majesty’s Government, (CMO for England and medical adviser to the United Kingdom government), the Northern Ireland Executive, the Scottish Government or the Welsh Government. |
||
|
Medical abortion |
2 medicines are taken. The first is mifepristone (antiprogesterone). The second is misoprostol (prostaglandin), which may be taken at the same time or within 3 days of the first medicine. |
||
|
Surgical abortion |
The pregnancy is removed in an operation by a doctor. There are 2 types. Vacuum aspiration used between 3 and 12 weeks, where the fetus is removed by suction. Dilatation and Evacuation, used between 13 and 24 weeks, where the fetus is removed using forceps. |
